Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (2): 497-504.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.0734
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Meiling PAN( ), Nannan SUN(
), Nannan SUN( ), Zhichao ZHAO
), Zhichao ZHAO
Received:2024-08-05
Revised:2024-09-13
Online:2025-02-28
Published:2025-03-18
Contact:
Nannan SUN
E-mail:panmeiling@hbwe.edu.cn;sunnannan@hbwe.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Meiling PAN, Nannan SUN, Zhichao ZHAO. Theoretical study of two-dimensional VC2 as an anode material for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(2): 497-504.
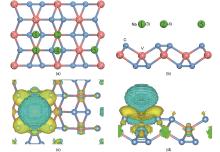
Fig.2
(a) Top and (b) side views of adsorption sites for the Na on VC2 monolayer (The green balls of numbers 1—5 indicate possible Na adsorption sites: pink represents the V atom; blue represents the C atom); (c) Top view and (d) side view of the charge density difference plot for Na adsorbed on VC2: Blue regions indicate electron loss;while the pink regions indicate electron gain"
Table 2
Adsorption energy, theoretical capacity, and diffusion barrier of some two-dimensional Na+ battery anode materials"
| Material type | Adsorption energy/eV | Theoretical capacity/(mAh/g) | Diffusion barrier/eV | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VC2 | 2.37 | 715 | 0.23 | This paper |
| ZrC2 | 0.96 | 932 | 0.02 | [ |
| 2H-SiC | 0.81 | 85 | 3.3 | [ |
| Ca2C | 2.84 | 582 | 0.06 | [ |
| Si3C | 0.72 | 1115 | 0.34 | [ |
| g-GeC | 1.26 | 633 | 0.06 | [ |
| SiC7 | 1.64 | 696 | 0.8 | [ |
| CuTe | 1.04 | 280 | 0.31~0.72 | [ |
| 锗醚 | 1.32 | 167 | 0.73 | [ |
| R57-BN | 1.55 | 662 | 0.55 | [ |
| 1 | LV X S, WEI W, SUN Q L, et al. A first-principles study of NbSe2 monolayer as anode materials for rechargeable lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2017, 50(23): 235501. DOI:10.1088/1361-6463/aa6eca. |
| 2 | LI M, LU J, CHEN Z W, et al. 30 years of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018: e1800561. DOI:10.1002/adma. 2018 00561. |
| 3 | WANG N N, BAI Z C, QIAN Y T, et al. Double-walled Sb@TiO2– x nanotubes as a superior high-rate and ultralong-lifespan anode material for Na-ion and Li-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(21): 4126-4133. DOI:10.1002/adma.201505918. |
| 4 | NAYAK P K, YANG L T, BREHM W, et al. From lithium-ion to sodium-ion batteries: Advantages, challenges, and surprises[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed), 2018, 57(1): 102-120. DOI:10.1002/anie.201703772. |
| 5 | KUNDU D P, TALAIE E, DUFFORT V, et al. The emerging chemistry of sodium ion batteries for electrochemical energy storage[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed), 2015, 54(11): 3431-3448. DOI:10.1002/anie.201410376. |
| 6 | LIANG J L, WEI C B, HUO D X, et al. Research progress on modification and application of two-dimensional anode materials for sodium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 85: 111044. DOI:10.1016/j.est.2024.111044. |
| 7 | 姚远, 宗若奇, 盖建丽. 钠离子电池锑基及铋基金属负极材料研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(8): 2649-2664. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.0180. |
| YAO Y, ZONG R Q, GAI J L. Research progress of antimony-and bismuth-based metallic anode materials for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(8): 2649-2664. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.0180. | |
| 8 | ER D Q, LI J W, NAGUIB M, et al. Ti3C2 MXene as a high capacity electrode material for metal (Li, Na, K, Ca) ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(14): 11173-11179. DOI:10.1021/am501144q. |
| 9 | WANG D S, GAO Y, LIU Y H, et al. Investigation of chloride ion adsorption onto Ti2C MXene monolayers by first-principles calculations[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(47): 24720-24727. DOI:10.1039/C7TA09057A. |
| 10 | FAN K, YING Y R, LI X Y, et al. Theoretical investigation of V3C2 MXene as prospective high-capacity anode material for metal-ion (Li, Na, K, and Ca) batteries[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2019, 123(30): 18207-18214. DOI:10.1021/acs.jpcc. 9b03963. |
| 11 | SUN Q L, DAI Y, MA Y D, et al. Ab initio prediction and characterization of Mo2C monolayer as anodes for lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2016, 7(6): 937-943. DOI:10.1021/acs.jpclett.6b00171. |
| 12 | WU Y T, NIE P, WANG J, et al. Few-layer MXenes delaminated via high-energy mechanical milling for enhanced sodium-ion batteries performance[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(45): 39610-39617. DOI:10.1021/acsami.7b12155. |
| 13 | KAJIYAMA S, SZABOVA L, SODEYAMA K, et al. Sodium-ion intercalation mechanism in MXene nanosheets[J]. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(3): 3334-3341. DOI:10.1021/acsnano.5b06958. |
| 14 | SUN D D, WANG M S, LI Z Y, et al. Two-dimensional Ti3C2 as anode material for Li-ion batteries[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2014, 47: 80-83. DOI:10.1016/j.elecom. 2014. 07.026. |
| 15 | YANG E, JI H, KIM J, et al. Exploring the possibilities of two-dimensional transition metal carbides as anode materials for sodium batteries[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2015, 17(7): 5000-5005. DOI:10.1039/C4CP05140H. |
| 16 | ZHAO T S, ZHANG S H, GUO Y G, et al. TiC2: A new two-dimensional sheet beyond MXenes[J]. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(1): 233-242. DOI:10.1039/c5nr04472c. |
| 17 | XU J, WANG D S, LIAN R Q, et al. Structural prediction and multilayer Li+ storage in two-dimensional VC2 carbide studied by first-principles calculations[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(15): 8873-8881. DOI:10.1039/c9ta01476d. |
| 18 | ZHANG F, JING T, CAI S H, et al. Two-dimensional ZrC2 as a novel anode material with high capacity for sodium ion battery[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2021, 23(22): 12731-12738. DOI:10.1039/d1cp00050k. |
| 19 | GIANNOZZI P, BARONI S, BONINI N, et al. QUANTUM ESPRESSO: A modular and open-source software project for quantum simulations of materials[J]. Journal of Physics Condensed Matter, 2009, 21(39): 395502. DOI:10.1088/0953-8984/21/39/395502. |
| 20 | PERDEW J P, BURKE K, WANG Y. Generalized gradient approximation for the exchange-correlation hole of a many-electron system[J]. Physical Review B, 1996, 54(23): 16533-16539. DOI:10.1103/physrevb.54.16533. |
| 21 | DUA H, DEB J, PAUL D, et al. Twin-graphene as a promising anode material for Na-ion rechargeable batteries[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2021, 4(5): 4912-4918. DOI:10.1021/acsanm. 1c00460. |
| 22 | MORTAZAVI M, WANG C, DENG J K, et al. Ab initio characterization of layered MoS2 as anode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 268: 279-286. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.06.049. |
| 23 | MAJID A, HUSSAIN K, KHAN S U, et al. First principles study of SiC as the anode in sodium ion batteries[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 44(21): 8910-8921. DOI:10.1039/D0NJ01311K. |
| 24 | JIANG H R, SHYY W, LIU M, et al. Boron phosphide monolayer as a potential anode material for alkali metal-based batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(2): 672-679. DOI:10.1039/C6TA09264K. |
| 25 | SHUKLA V, JENA N K, NAQVI S R, et al. Modelling high-performing batteries with mxenes: The case of S-functionalized two-dimensional nitride mxene electrode[J]. Nano Energy, 2019, 58: 877-885. DOI:10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.02.007. |
| 26 | RAJPUT K, KUMAR V, THOMAS S, et al. Ca2C MXene monolayer as a superior anode for metal-ion batteries[J]. 2D Materials, 2021, 8(3): 035015. DOI:10.1088/2053-1583/abf233. |
| 27 | WANG Y N, LI Y S. Ab initio prediction of two-dimensional Si3C enabling high specific capacity as an anode material for Li/Na/K-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(8): 4274-4282. DOI:10.1039/c9ta11589g. |
| 28 | KHOSSOSSI N, BANERJEE A, ESSAOUDI I, et al. Thermody namics and kinetics of 2D g-GeC monolayer as an anode materials for Li/Na-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 485: 229318. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2020. 229318. |
| 29 | YADAV N, CHAKRABORTY B, DHILIP KUMAR T J. First-principles design and investigation of siligraphene as a potential anode material for Na-ion batteries[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2020, 124(21): 11293-11300. DOI:10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c00847. |
| 30 | LING F L, LIU X Q, LI L, et al. Novel CuTe monolayer as promising anode material for Na-ion batteries: A theoretical study[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 573: 151550. DOI:10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151550. |
| 31 | 陈思钰, 叶小娟, 刘春生. 二维锗醚在钠离子电池方面的理论研究[J]. 物理学报, 2022, 71(22): 352-360. DOI: 10.7498/aps. 71. 20220572. |
| CHEN S Y, YE X J, LIU C S. Theoretical research of two-dimensional germanether in sodium-ion battery[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2022, 71(22): 352-360. DOI: 10.7498/aps.71.20220572. | |
| 32 | 王文春, 马天赐, 刘春生. 二维半导体R57-BN作为钠离子电池阳极材料的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(6): 93-100. |
| WANG W C, MA T C, LIU C S. Theoretical research of two-dimensional semiconductor R57-BN as anode material of sodium-ion battery[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(6): 93-100. | |
| 33 | 曹美兰, 侯晓川, 周玉, 等. 钠离子电池用层状氧化物空气稳定性研究进展[J]. 电池, 2024, 54(1): 116-120. DOI: 10.19535/j.1001-1579.2024.01.026. |
| CAO M L, HOU X C, ZHOU Y, et al. Research progress in air stability of layered oxide for sodium-ion battery[J]. Dianchi(Battery Bimonthly), 2024, 54(1): 116-120. DOI: 10.19535/j.1001-1579.2024.01.026. |
| [1] | Lijun FAN, Baozhou WU, Kejun CHEN. Controllable synthesis of FeS2 with different morphologies and their sodium storage performances [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(8): 2541-2549. |
| [2] | Shirong TAN, Wenji YIN, Cuihong ZENG, Xiaoqiong LI, Shuo QI, Fangli JI, Sijiang HU, Hongqiang WANG, Qingyu LI. Role of high temperature quenching in structure and performance of Mn-based layered cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2399-2406. |
| [3] | Lifeng WANG, Naiqing REN, Hai YANG, Yu YAO, Yan YU. Advances in low-temperature electrolytes for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2206-2223. |
| [4] | Dan LI, Tie MA, Hanhao LIU, Li GUO. Carbon-coated nano-bismuth as high-rate sodium anode material [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(6): 1775-1785. |
| [5] | Qingyi LIU. Energy storage mechanism and performance enhancement strategies of sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(6): 1871-1873. |
| [6] | Yiwei ZHAO, Fuhua ZHANG, Shun YAN, Kun DING, Haifeng LAN, Hui LIU. Research progress on the conductivity of Prussian blue sodium-ion battery cathode materials [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(5): 1474-1486. |
| [7] | Yinchen YANG, Shanling REN, Zhihong YANG, Yunhui WANG. First principles study of two-dimensional boron antimony films as anchoring materials for lithium-sulfur batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(9): 2760-2766. |
| [8] | Zinan ZHANG, Jian CHEN. Preparation and property evaluation of Nb-doped Na3V2O2 (PO4 ) 2F hollow microspheres as cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(8): 2370-2381. |
| [9] | Yuhua BIAN, Zhaomeng LIU, Xuanwen GAO, Jianguo LI, Da WANG, Shangzhuo LI, Wenbin LUO. Role of CoS2/NC in ether-based electrolytes as high-performance anodes for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1500-1509. |
| [10] | Na CHEN, Anqi LI, Zixiang GUO, Yuzhe ZHANG, Xue QIN. Research progress on the construction and optimization of Prussian blue material structure for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(11): 3340-3351. |
| [11] | ZHANG Haoran, CHE Haiying, GUO Kaiqiang, SHEN Zhan, ZHANG Yunlong, CHEN Hangda, ZHOU Huang, LIAO Jianping, LIU Haimei, MA Zifeng. Preparation of Sn-doped NaNi1/3Fe1/3Mn1/3-x Sn x O2 cathode materials and their electrochemical performance [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1874-1882. |
| [12] | Dangling LIU, Shimin WANG, Zhihui GAO, Lufu XU, Shubiao XIA, Hong GUO. Properties of three-dimensional NZSPO/PAN-[PEO-NATFST] sodium-battery-composite solid electrolyte [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(3): 931-937. |
| [13] | Huanqing LIU, Xu GAO, Jun CHEN, Shouyi YIN, Kangyu ZOU, Laiqiang XU, Guoqiang ZOU, Hongshuai HOU, Xiaobo JI. Layered oxide cathode for sodium ion batteries: Interlayer glide, phase transition and performance [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(5): 1327-1339. |
| [14] | Shu GAO, Min ZHOU, Jing HAN, Cong GUO, Yuan TAN, Kai JIANG, Kangli WANG. Progress on polymer electrolyte in sodium ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(5): 1300-1308. |
| [15] | Xianghua ZHANG, Wei LUO, Xianhong RUI, Yan YU. Preparation and electrochemical performance of VOPO4·2H2O nanosheet cathode for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(5): 1410-1415. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
