Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (2): 462-479.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0614
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiuli GUO1( ), Xiaolong ZHOU1, Caineng ZOU2(
), Xiaolong ZHOU1, Caineng ZOU2( ), Yongbing TANG1(
), Yongbing TANG1( )
)
Received:2023-09-11
Revised:2023-09-28
Online:2024-02-28
Published:2024-03-01
Contact:
Caineng ZOU, Yongbing TANG
E-mail:guo@siat.ac.cn;zcn@petrochina.com.cn;tangyb@siat.ac.cn
CLC Number:
Xiuli GUO, Xiaolong ZHOU, Caineng ZOU, Yongbing TANG. Research progress and perspectives of aqueous dual-ions batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(2): 462-479.
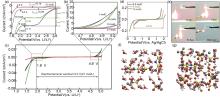
Fig. 2
(a)—(c) Electrochemical stability window of LiTFSI-H2O electrolyte with different concentrations on the inactive electrode[21]; (d) Electrochemical stability window ofthe elyctrolyte containing 15 mol/L Al(ClO4)3 [24]; (e) Flammability test of 8 mol/L Zn (ClO4)2 “water in salt” electrolyte[26]; (f), (g) The solvation structure of Zn2+ ions in the electrolytes containing 5 mol/L LiTFSI and 20 mol/L LiTFSI, respectively(Grey: Zn2+, red: O, white: H; Yellow: S, Blue: N, Cyan: C, Pink: F)26]"
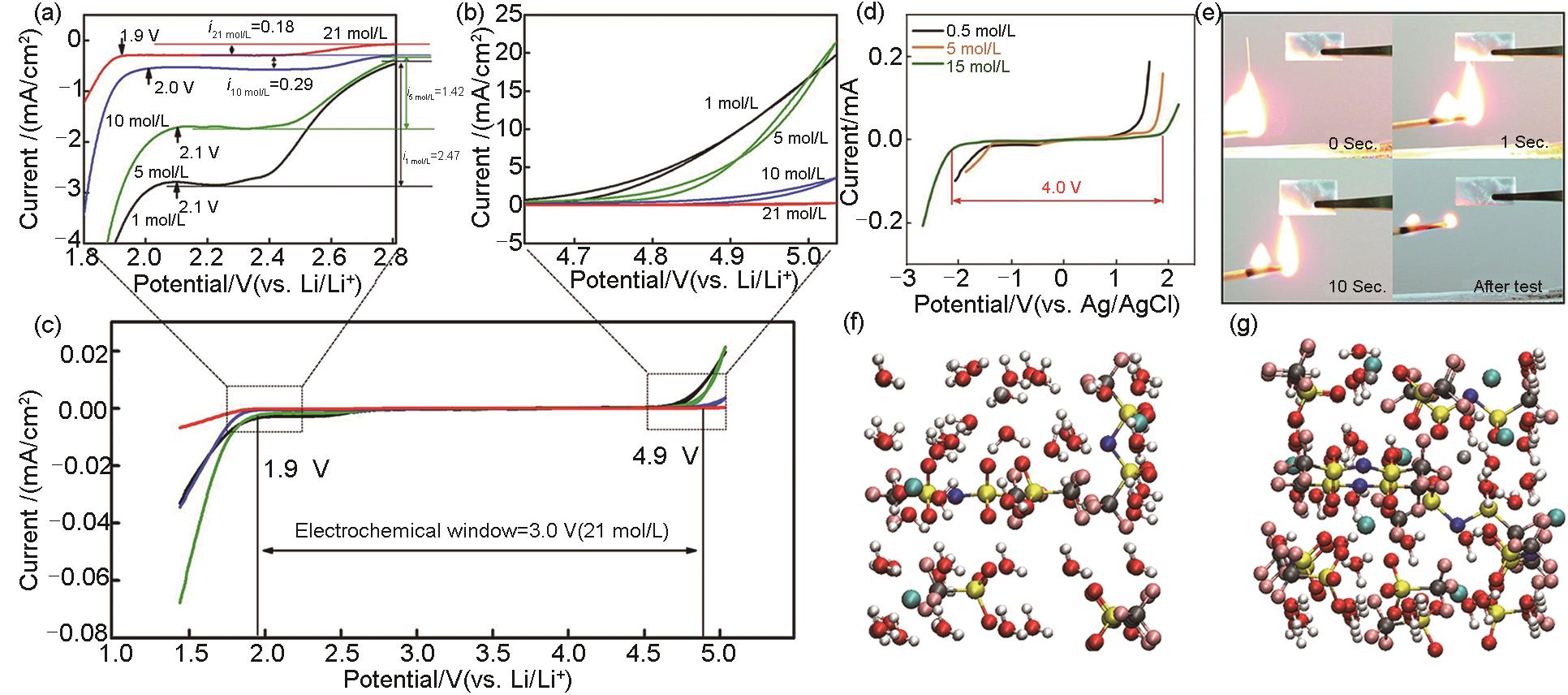
Fig. 3
(a) Schematic of ADIBs constructed by KS6 and AC in Water-in-Bisalt electrolyte of LiFSI-LiTFSI[27]; (b)—(d) CV curves of PTCDI-G electrode in the electrolytes containing NaBF4, NaOTf, and NaTFSI at a scanning speed of 5 mV/s[29]; (e) The charging and discharging curves of Zn||graphite batteries at a current density of 100—5000 mA/g (1—50 C)[28]; (f) Calculated raman models of [Mg(H2O)6]2+, [MgCl4]2-, and [MgCl3(H2O)]-(yellow: Mg, red: O, green: Cl)[33]; (g) TEM images of fully charged graphite cathode[33]; (h) Photograph of the aqueous electrolyte consisted of 25 mol/L ZnCl2, 25 mol/L ZnBr2, and 25 mol/L Zn(OAc)2[39]; (i) Schematic of the ZIS-PVA hydrogel electrolytes in Zn||PANI ADIBs[41]; (j) Schematic overview of active materials for aqueous LIBs (white) and DIBs (yellow) with respect to their redox potentials (0 V vs. Ag/AgCl = 3.24 V vs. Li/Li+) and practical capacities related to the electrochemical stability windows of water-based electrolytes[42]; (k) Combustion test photos of aqueous/organic hybrid electrolyte[43]"
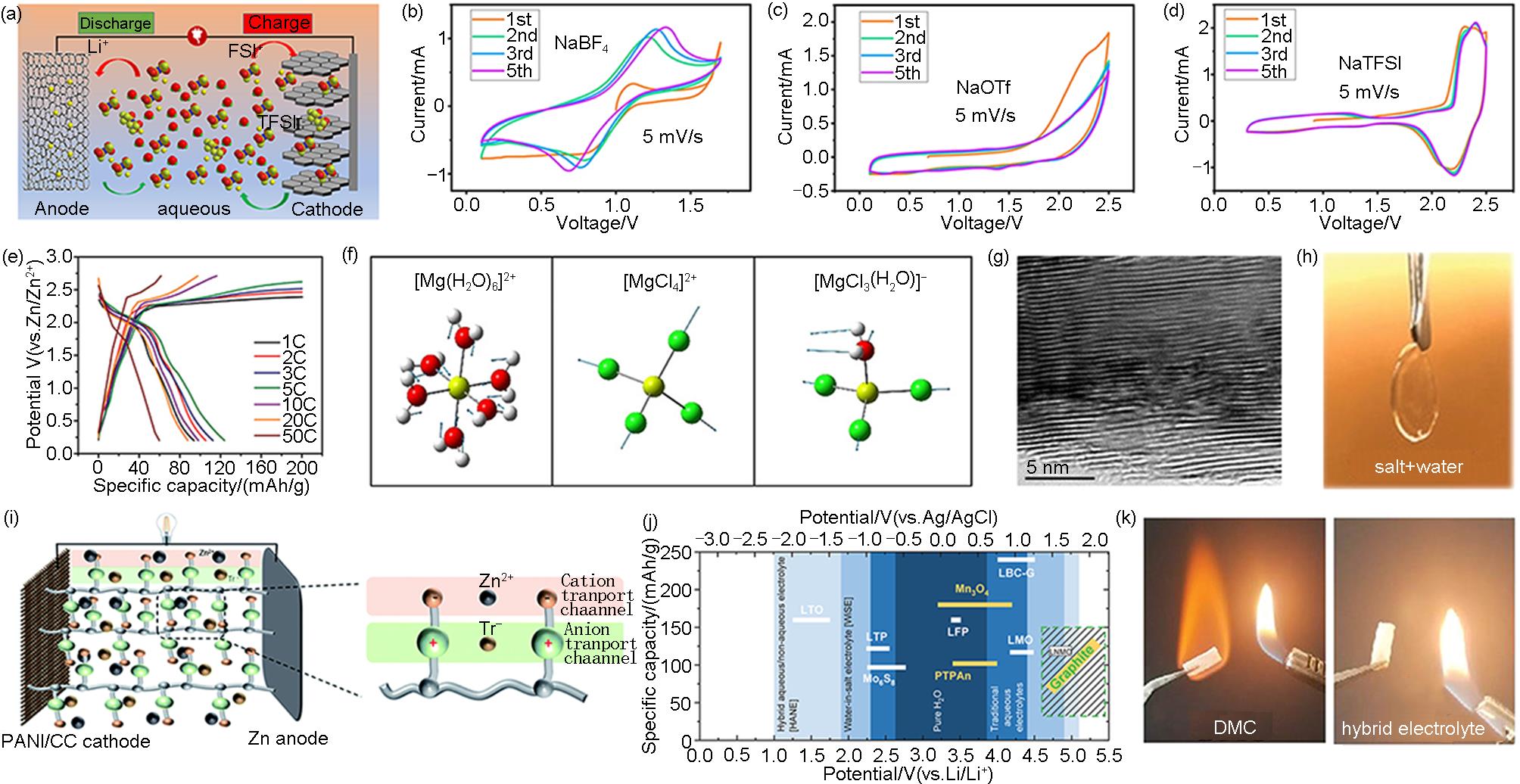

Fig. 4
(a) Structure diagram of anionic graphite intercalation compound[44]; (b), (c) Schematic illustration of the preparation process of a free-standing graphite electrode and corresponding SEM image[47]; (d), (e) schematics of a Zn||graphite battery[6, 28]; (f), (g) Schematic illustration of the synthetic procedure for NFG and relevant TEM image[51]"
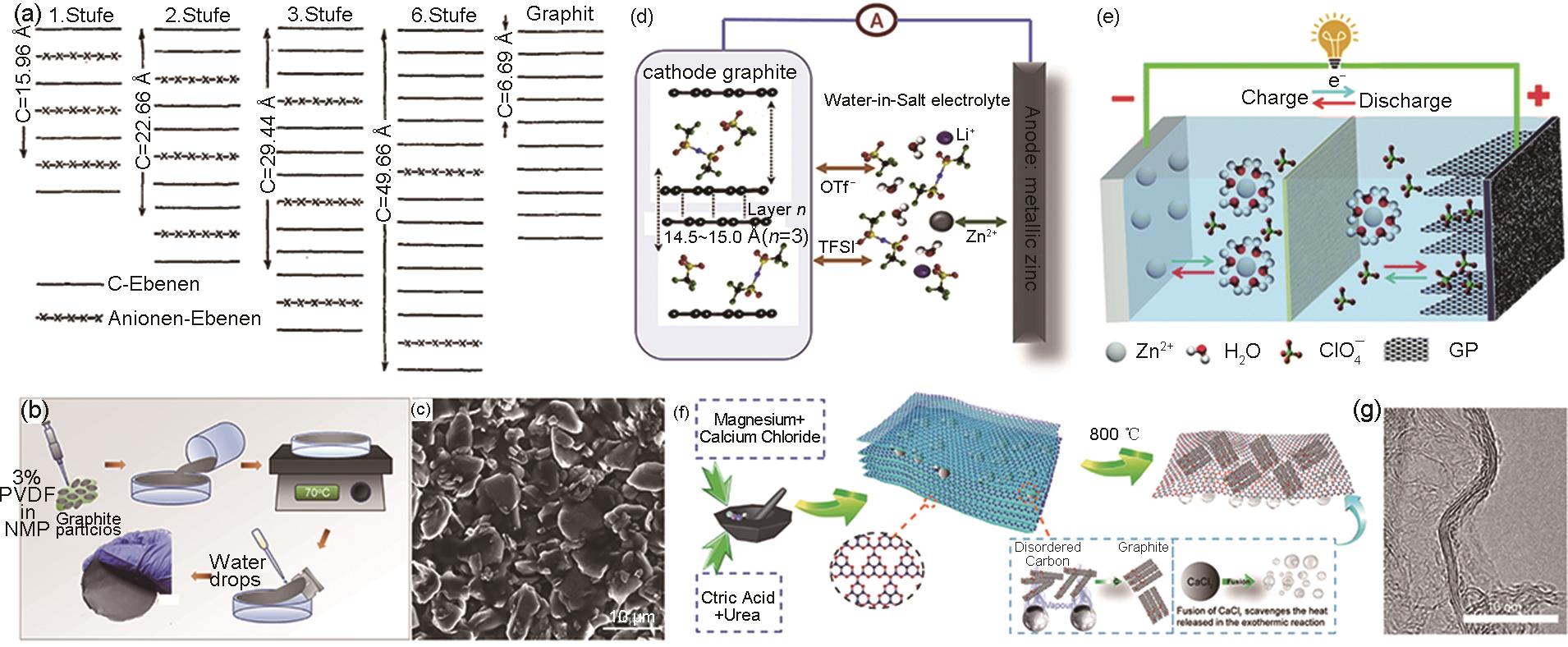

Fig. 5
(a) Electrochemical reaction mechanism of PANI[55]; (b) Optical image of assembled Zn-PANI batteries in ring-, H-, and cylindrical shapes; (c) Cell voltage of spherical Zn-PANI battery; (d) Picture of two H-shaped Zn-PANI batteries in series light the LEDs[56]; (e) Structure and reaction active site of m-PTPA, pink suggests high electron density[59]"
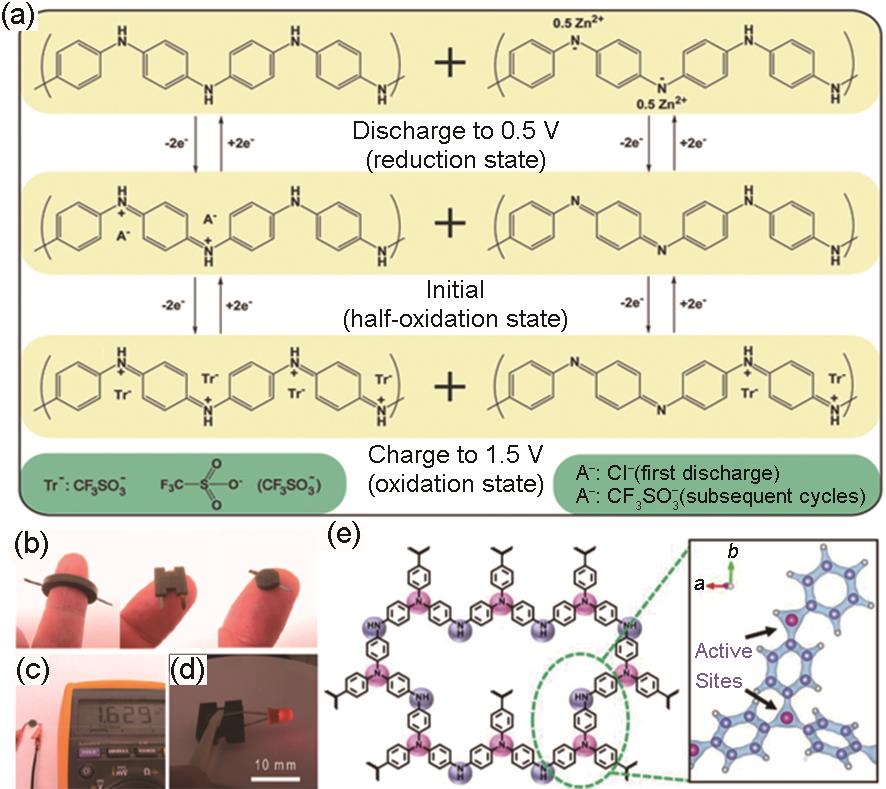
Fig. 6
(a) The proposed charge/discharge mechanism of zinc/polyindole battery[60]; (b) Schematic representation of anionic storage mechanism for PANMTh[63]; (c) Two-step oxidation/reduction of BDB(A-: OTf-/TFSI-)[64]; (d), (e) Charge-discharge profiles and long cycling performance of Zn-BDB battery[64]; (f) Redox mechanism of PTVE with anions[66]; (g) LUMO and HOMO of the oxidation state of a PTVE unit[66]"


Fig. 7
(a) The charge storage mechanism of PDB cathode[67]; (b), (c) SEI-forming mechanism on PDB electrode[68]; (d) The charge storage mechanism of PTD-1 in 2mol/L ZnSO4/H2O electrolyte[69]; (e) Rate performance of the Zn||PTD-1 cell in the voltage range of 0.1—1.8 V (vs. Zn/Zn2+)[69]; (f) Scheme of the preparation process of P/G[70]; (g), (h) Ex situ FTIR spectra at different SOC and structure of coronene[71]; (i), (j) The energy levels and corresponding HOMO diagram of LPy-1, LPy-2 and CLPy[71]; (k), (l) Rate performance and long cycling life of Zn||CLPy battery[72]"

Fig. 8
(a) Schematic of the device and reaction mechanism of Zn-I ADIBs[76]; (b) Crystal structure of Zn-TCPP[77]; (c) CV curves of Mn3O4 cathode at scan rate of 3 mV/s (top) and its corresponding electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance curve (bottom) in the 2nd cycle. Black: anodic scan, red and blue: cathodic scan[78]; (d) Diagram of the generic counter-ion insertion electrode structures mechanism[79]; (e) Schematic diagram of reaction mechanism of Na3V2(PO4)3 electrode[82]; (f) Structure diagram of NTP@C||NNH ADIBs[83]; (g) Schematic illustration of the charge storage mechanism of the NiFe-LDH/CNT (+)||NaOH (aq)||NTP@C (-) battery[84]"


Fig. 9
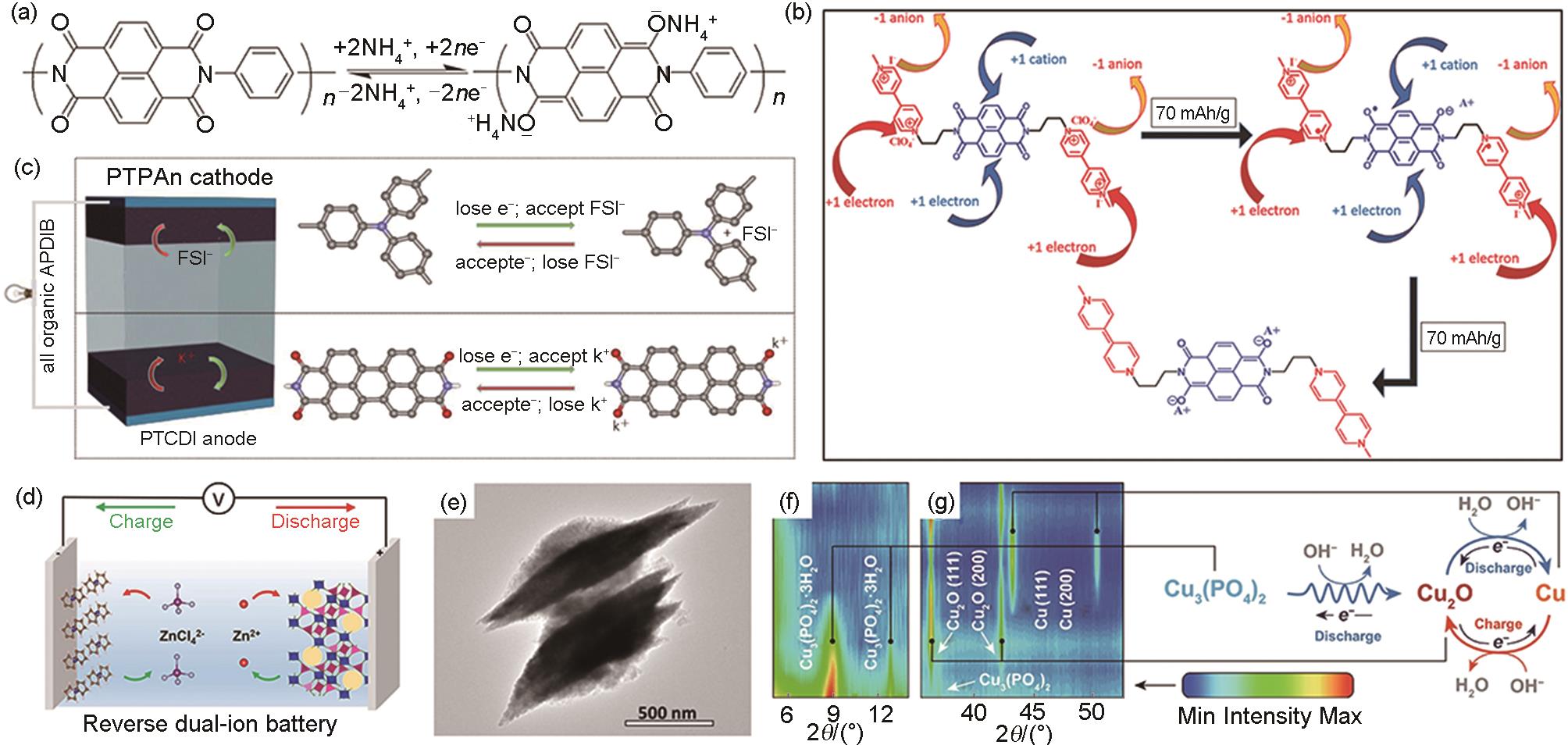
(a) The storage mechanism of NH4+ in PI electrode[59]; (b) Charge storage mechanism of MNV in aqueous electrolyte[90]; (c) Schematic diagram of PTCDI||PTPAn ADIBs device structure and charge storage process[58]; (d) Working mechanism diagram of reverse dual ion battery assembled with Fc/C anode and Zn3[Fe(CN)6]2 cathode[8]; (e) TEM image of Fe2O3[91]; (f), (g) The in-situ XRD patterns of Cu3(PO4)2 electrode and reasonable electrochemical reaction mechanism[92]"
| 1 | LI W J, YU X Z, HU N, et al. Study on the relationship between fossil energy consumption and carbon emission in Sichuan Province[J]. Energy Reports, 2022, 8: 53-62. |
| 2 | LARCHER D, TARASCON J M. Towards greener and more sustainable batteries for electrical energy storage[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2015, 7: 19-29. |
| 3 | DUAN J, TANG X, DAI H F, et al. Building safe lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles: A review[J]. Electrochemical Energy Reviews, 2020, 3(1): 1-42. |
| 4 | ZENG X L, LI J H, LIU L L. Solving spent lithium-ion battery problems in China: Opportunities and challenges[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2015, 52: 1759-1767. |
| 5 | JU Z N, ZHAO Q, CHAO D L, et al. Energetic aqueous batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(27): 2201074. |
| 6 | ZHANG H, LIU X, QIN B S, et al. Electrochemical intercalation of anions in graphite for high-voltage aqueous zinc battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 449: 227594. |
| 7 | OU X W, GONG D C, HAN C J, et al. Advances and prospects of dual-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(46): 2102498. |
| 8 | WU X Y, XU Y K, ZHANG C, et al. Reverse dual-ion battery via a ZnCl2 water-in-salt electrolyte[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(15): 6338-6344. |
| 9 | CHEN Y Q, KANG Y Q, ZHAO Y, et al. A review of lithium-ion battery safety concerns: The issues, strategies, and testing standards[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 59: 83-99. |
| 10 | WANG Q S, JIANG L H, YU Y, et al. Progress of enhancing the safety of lithium ion battery from the electrolyte aspect[J]. Nano Energy, 2019, 55: 93-114. |
| 11 | ZHANG H, LIU X, LI H H, et al. Challenges and strategies for high-energy aqueous electrolyte rechargeable batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2021, 60(2): 598-616. |
| 12 | CHEN C, LEE C S, TANG Y B. Fundamental understanding and optimization strategies for dual-ion batteries: A review[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2023, 15(1): 121. |
| 13 | KIM H, HONG J, PARK K Y, et al. Aqueous rechargeable Li and Na ion batteries[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(23): 11788-11827. |
| 14 | PLACKE T, HECKMANN A, SCHMUCH R, et al. Perspective on performance, cost, and technical challenges for practical dual-ion batteries[J]. Joule, 2018, 2(12): 2528-2550. |
| 15 | CHAO D L, ZHOU W H, XIE F X, et al. Roadmap for advanced aqueous batteries: From design of materials to applications[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(21): eaba4098. |
| 16 | LIU J L, XU C H, CHEN Z, et al. Progress in aqueous rechargeable batteries[J]. Green Energy & Environment, 2018, 3(1): 20-41. |
| 17 | EFTEKHARI A. High-energy aqueous lithium batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(24): 1801156. |
| 18 | ZHANG H, GUO G L, ADENUSI H, et al. Advances and issues in developing intercalation graphite cathodes for aqueous batteries[J]. Materials Today, 2022, 53: 162-172. |
| 19 | WANG S F, GUAN Y, GAN F Q, et al. Charge carriers for aqueous dual-ion batteries[J]. ChemSusChem, 2023, 16(4): e202201373. |
| 20 | BORODIN O, SELF J, PERSSON K A, et al. Uncharted waters: Super-concentrated electrolytes[J]. Joule, 2020, 4(1): 69-100. |
| 21 | SUO L M, BORODIN O, GAO T, et al. "Water-in-salt" electrolyte enables high-voltage aqueous lithium-ion chemistries[J]. Science, 2015, 350(6263): 938-943. |
| 22 | KONDO Y, MIYAHARA Y, FUKUTSUKA T, et al. Electrochemical intercalation of bis(fluorosulfonyl)amide anions into graphite from aqueous solutions[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2019, 100: 26-29. |
| 23 | ZHU Y P, YIN J, EMWAS A H, et al. An aqueous Mg2+-based dual-ion battery with high power density[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(50): 2107523. |
| 24 | ALI ZAFAR Z, ABBAS G, SILHAVIK M, et al. Reversible anion intercalation into graphite from aluminum perchlorate "water‐in‐salt" electrolyte[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2022, 404: 139754. |
| 25 | ALI ZAFAR Z, ABBAS G, KNIZEK K, et al. Chaotropic anion based "water-in-salt" electrolyte realizes a high voltage Zn-graphite dual-ion battery[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(4): 2064-2074. |
| 26 | CLARISZA A, BEZABH H K, JIANG S K, et al. Highly concentrated salt electrolyte for a highly stable aqueous dual-ion zinc battery[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(32): 36644-36655. |
| 27 | LI H, KURIHARA T, YANG D Y, et al. A novel aqueous dual-ion battery using concentrated bisalt electrolyte[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 38: 454-461. |
| 28 | RODRÍGUEZ-PÉREZ I A, ZHANG L, WROGEMANN J M, et al. Enabling natural graphite in high-voltage aqueous graphite || Zn metal dual-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(41): 2001256. |
| 29 | HUANG Z D, HOU Y, WANG T R, et al. Manipulating anion intercalation enables a high-voltage aqueous dual ion battery[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 3106. |
| 30 | PUTTASWAMY R, MONDAL C, MONDAL D, et al. An account on the deep eutectic solvents-based electrolytes for rechargeable batteries and supercapacitors[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2022, 33: e00477. |
| 31 | SMITH E L, ABBOTT A P, RYDER K S. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and their applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(21): 11060-11082. |
| 32 | WU J X, LIANG Q H, YU X L, et al. Deep eutectic solvents for boosting electrochemical energy storage and conversion: A review and perspective[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(22): 2011102. |
| 33 | KIM K I, GUO Q B, TANG L T, et al. Reversible insertion of Mg-Cl superhalides in graphite as a cathode for aqueous dual-ion batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2020, 59(45): 19924-19928. |
| 34 | SCHMUELLING G, PLACKE T, KLOEPSCH R, et al. X-ray diffraction studies of the electrochemical intercalation of bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide anions into graphite for dual-ion cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 239: 563-571. |
| 35 | MEISTER P, SIOZIOS V, REITER J, et al. Dual-ion cells based on the electrochemical intercalation of asymmetric fluorosulfonyl-(trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide anions into graphite[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 130: 625-633. |
| 36 | KIM K I, TANG L T, MIRABEDINI P, et al. [LiCl2]– superhalide: A new charge carrier for graphite cathode of dual-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(23): 2112709. |
| 37 | WROGEMANN J M, KÜNNE S, HECKMANN A, et al. Development of safe and sustainable dual-ion batteries through hybrid aqueous/nonaqueous electrolytes[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(8): 1902709. |
| 39 | KIM K I, TANG L T, MURATLI J M, et al. A Graphite∥PTCDI aqueous dual-ion battery[J]. ChemSusChem, 2022, 15(5): e202102394. |
| 40 | WANG Z F, LI H F, TANG Z J, et al. Hydrogel electrolytes for flexible aqueous energy storage devices[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(48): 1804560. |
| 41 | CAI S Y, CHU X Y, LIU C, et al. Water-salt oligomers enable supersoluble electrolytes for high-performance aqueous batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(13): e2007470. |
| 42 | LI L W, ZHANG L S, GUO W B, et al. High-performance dual-ion Zn batteries enabled by a polyzwitterionic hydrogel electrolyte with regulated anion/cation transport and suppressed Zn dendrite growth[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(43): 24325-24335. |
| 43 | ZHU J J, XU Y T, FU Y J, et al. Hybrid aqueous/nonaqueous water-in-bisalt electrolyte enables safe dual ion batteries[J]. Small, 2020, 16(17): e1905838. |
| 44 | RÜDORFF W, HOFMANN U. Über graphitsalze[J]. Zeitschrift Für Anorganische Und Allgemeine Chemie, 1938, 238(1): 1-50. |
| 45 | WESSBECHER SKAF D, EDWARDS J K. Electrochemical graphite intercalation with nitric acid solutions[J]. Synthetic Metals, 1992, 46(2): 137-145. |
| 46 | NOEL M, SANTHANAM R, FRANCISCA FLORA M. Comparison of fluoride intercalation/de-intercalation processes on graphite electrodes in aqueous and aqueous methanolic HF media[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 1995, 56(2): 125-131. |
| 47 | SHPIGEL N, MALCHIK F, LEVI M D, et al. New aqueous energy storage devices comprising graphite cathodes, MXene anodes and concentrated sulfuric acid solutions[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 32: 1-10. |
| 48 | SEEL J A, DAHN J R. Electrochemical intercalation of PF6 into graphite[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2000, 147(3): 892. |
| 49 | ZHOU X L, LIU Q R, JIANG C L, et al. Strategies towards low-cost dual-ion batteries with high performance[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2020, 59(10): 3802-3832. |
| 50 | YANG H, SHI X Y, DENG T, et al. Carbon-based dual-ion battery with enhanced capacity and cycling stability[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2018, 5(23): 3612-3618. |
| 51 | GUO Q B, KIM K I, JIANG H, et al. A high-potential anion-insertion carbon cathode for aqueous zinc dual-ion battery[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(38): 2002825. |
| 52 | LU Y, CHEN J. Prospects of organic electrode materials for practical lithium batteries[J]. Nature Reviews Chemistry, 2020, 4: 127-142. |
| 53 | XU Y, ZHOU M, LEI Y. Organic materials for rechargeable sodium-ion batteries[J]. Materials Today, 2018, 21(1): 60-78. |
| 54 | SONG Z P, ZHOU H S. Towards sustainable and versatile energy storage devices: An overview of organic electrode materials[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2013, 6(8): 2280-2301. |
| 55 | WAN F, ZHANG L L, WANG X Y, et al. An aqueous rechargeable zinc-organic battery with hybrid mechanism[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(45): 1804975. |
| 56 | KIM C, AHN B Y, WEI T S, et al. High-power aqueous zinc-ion batteries for customized electronic devices[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(12): 11838-11846. |
| 57 | ZHOU G Y, AN X Y, ZHOU C Y, et al. Highly porous electroactive polyimide-based nanofibrous composite anode for all-organic aqueous ammonium dual-ion batteries[J]. Composites Communications, 2020, 22: 100519. |
| 58 | GE J M, YI X H, FAN L, et al. An all-organic aqueous potassium dual-ion battery[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 57: 28-33. |
| 59 | ZHANG H Z, ZHONG L F, XIE J H, et al. A COF-like N-rich conjugated microporous polytriphenylamine cathode with pseudocapacitive anion storage behavior for high-energy aqueous zinc dual-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(34): e2101857. |
| 60 | CAI Z J, HOU C W. Study on the electrochemical properties of zinc/polyindole secondary battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(24): 10731-10736. |
| 61 | CHEN C X, GAN Z Y, XU C, et al. Electrosynthesis of poly(aniline-co-azure B) for aqueous rechargeable zinc-conducting polymer batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 252: 226-234. |
| 62 | MU S L, SHI Q F. Controllable preparation of poly(aniline-co-5-aminosalicylic acid) nanowires for rechargeable batteries[J]. Synthetic Metals, 2016, 221: 8-14. |
| 63 | CHEN C X, HONG X Z, CHEN A K, et al. Electrochemical properties of poly(aniline-co-N-methylthionine) for zinc-conducting polymer rechargeable batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 190: 240-247. |
| 64 | GLATZ H, LIZUNDIA E, PACIFICO F, et al. An organic cathode based dual-ion aqueous zinc battery enabled by a cellulose membrane[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2019, 2(2): 1288-1294. |
| 65 | KOSHIKA K, SANO N, OYAIZU K, et al. An aqueous, electrolyte-type, rechargeable device utilizing a hydrophilic radical polymer-cathode[J]. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics, 2009, 210(22): 1989-1995. |
| 66 | LUO Y W, ZHENG F P, LIU L J, et al. A high-power aqueous zinc-organic radical battery with tunable operating voltage triggered by selected anions[J]. ChemSusChem, 2020, 13(9): 2239-2244. |
| 67 | XIE J, YU F, ZHAO J W, et al. An irreversible electrolyte anion-doping strategy toward a superior aqueous Zn-organic battery[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 33: 283-289. |
| 68 | LIN Z Q, FAN G H, ZHANG T, et al. Solid-electrolyte interphase for ultra-stable aqueous dual-ion storage[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(7): 2203532. |
| 69 | WANG N, GUO Z W, NI Z G, et al. Molecular tailoring of an n/p-type phenothiazine organic scaffold for zinc batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2021, 60(38): 20826-20832. |
| 70 | ZHANG H, XU D X, WANG L P, et al. A polymer/graphene composite cathode with active carbonyls and secondary amine moieties for high-performance aqueous Zn-organic batteries involving dual-ion mechanism[J]. Small, 2021, 17(25): e2100902. |
| 71 | RODRÍGUEZ-PÉREZ I A, ZHANG L, LEONARD D P, et al. Aqueous anion insertion into a hydrocarbon cathode via a water-in-salt electrolyte[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2019, 109: 106599. |
| 72 | ZHANG C, MA W Y, HAN C Z, et al. Tailoring the linking patterns of polypyrene cathodes for high-performance aqueous Zn dual-ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(1): 462-472. |
| 73 | ZHANG F, ZHANG G W, YAO H, et al. Scalable in situ growth of self-assembled coordination supramolecular network arrays: A novel high-performance energy storage material[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 338: 230-239. |
| 74 | AUBREY M L, LONG J R. A dual-ion battery cathode via oxidative insertion of anions in a metal-organic framework[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(42): 13594-13602. |
| 75 | WANG Z H, YAO H, ZHANG F, et al. Electro-synthesized Ni coordination supermolecular-networks-coated exfoliated graphene composite materials for high-performance asymmetric supercapacitors[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(42): 16476-16483. |
| 76 | TAN Y M, TAO Z R, ZHU Y F, et al. Anchoring I3 - via charge-transfer interaction by a coordination supramolecular network cathode for a high-performance aqueous dual-ion battery[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(42): 47716-47724. |
| 77 | TAN Y M, CHEN Z, TAO Z R, et al. A two-dimensional porphyrin coordination supramolecular network cathode for high-performance aqueous dual-ion battery[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2023, 62(12): e202217744. |
| 78 | JIANG H, WEI Z X, MA L, et al. An aqueous dual-ion battery cathode of Mn3O4 via reversible insertion of nitrate[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(16): 5286-5291. |
| 79 | JIANG H, JI X L. Counter-ion insertion of chloride in Mn3O4 as cathode for dual-ion batteries: A new mechanism of electrosynthesis for reversible anion storage[J]. Carbon Energy, 2020, 2(3): 437-442. |
| 80 | XU X Q, YANG H Q, WANG X L, et al. Efficient high-rate aqueous alkaline battery with dual-ion intercalation chemistry enabled by asymmetric electrode polarization[J]. Cell Reports Physical Science, 2022, 3(8): 100981. |
| 81 | CAO X X, PAN A Q, YIN B, et al. Nanoflake-constructed porous Na3V2(PO4)3/C hierarchical microspheres as a bicontinuous cathode for sodium-ion batteries applications[J]. Nano Energy, 2019, 60: 312-323. |
| 82 | SONG W X, JI X B, WU Z P, et al. First exploration of Na-ion migration pathways in the NASICON structure Na3V2(PO4)3[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(15): 5358-5362. |
| 83 | NI Q, GUO Q B, REN H X, et al. Realizing the multi-electron reaction in the Na3V2(PO4)3 cathode via reversible insertion of dihydrogen phosphate anions[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(1): 1233-1240. |
| 84 | NIAN Q S, LIU S, LIU J, et al. All-climate aqueous dual-ion hybrid battery with ultrahigh rate and ultralong life performance[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2019, 2(6): 4370-4378. |
| 85 | SONG F, HU X L. Exfoliation of layered double hydroxides for enhanced oxygen evolution catalysis[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 4477. |
| 86 | LEE P K, TAN T, WANG S, et al. Robust micron-sized silicon secondary particles anchored by polyimide as high-capacity, high-stability Li-ion battery anode[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(40): 34132-34139. |
| 87 | TIAN B B, ZHENG J, ZHAO C X, et al. Carbonyl-based polyimide and polyquinoneimide for potassium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(16): 9997-10003. |
| 88 | JIANG B, KONG T Y, CAI Z H, et al. In-situ modification of polyimide anode materials in dual-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2022, 435: 141402. |
| 89 | ZHANG Y D, AN Y F, YIN B, et al. A novel aqueous ammonium dual-ion battery based on organic polymers[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(18): 11314-11320. |
| 90 | PERTICARARI S, SAYED-AHMAD-BARAZA Y, EWELS C, et al. Dual anion-cation reversible insertion in a bipyridinium-diamide triad as the negative electrode for aqueous batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(8): 1701988. |
| 91 | TAO Y P, DING C X, TAN D M, et al. Aqueous dual-ion battery based on a hematite anode with exposed{1 0 4}facets[J]. ChemSusChem, 2018, 11(24): 4269-4274. |
| 92 | WU C, KOPOLD P, DING Y L, et al. Synthesizing porous NaTi2(PO4)3 nanoparticles embedded in 3D graphene networks for high-rate and long cycle-life sodium electrodes[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(6): 6610-6618. |
| 93 | CHEN S Q, WU C, SHEN L F, et al. Challenges and perspectives for NASICON-type electrode materials for advanced sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(48): 1700431. |
| 94 | ZHANG Z S, HU X Q, ZHOU Y, et al. Aqueous rechargeable dual-ion battery based on fluoride ion and sodium ion electrochemistry[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(18): 8244-8250. |
| 95 | YU H X, DENG C C, YAN H H, et al. Cu3(PO4)2: Novel anion convertor for aqueous dual-ion battery[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2021, 13(1): 41. |
| [1] | Shuyuan CHEN, Chen CHENG, Xiao XIA, Huanxin JU, Liang ZHANG. Research progress in the X-ray spectroscopy investigation of cathode materials for high-energy-density secondary batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(1): 113-129. |
| [2] | Zhuo LI, Xin GUO. Solidification of polymer-based electrolytes for energy-density solid-state batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(1): 212-230. |
| [3] | Yonghui ZHANG, Jie FU, Xianfeng LI, Changkun ZHANG. Research progress on in-situ characterization techniques for aqueous organic flow batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(9): 2971-2984. |
| [4] | Huan LIU, Na PENG, Qingwen GAO, Wenpeng LI, Zhirong YANG, Jingtao WANG. Crown ether-doped polymer solid electrolyte for high-performance all-solid-state lithium batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(8): 2401-2411. |
| [5] | Zhihao LIU, Tong DU, Ruirui LI, Tao DENG. Developments of wide temperature range, high voltage and safe EC-free electrolytes [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(8): 2504-2525. |
| [6] | Qixin GAO, Jingteng ZHAO, Guoxing LI. Research progress on fast-charging lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(7): 2166-2184. |
| [7] | Lingfeng HUANG, Dongmei HAN, Sheng HUANG, Shuanjin WANG, Min XIAO, Yuezhong MENG. Research progress of polymer electrolytes containing organoboron for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(6): 1815-1830. |
| [8] | Yuwen ZHAO, Huan YANG, Junpeng GUO, Yi ZHANG, Qi SUN, Zhijia ZHANG. Application of magnetic metal elements in sodium ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1332-1347. |
| [9] | Xuanchen WANG, Da WANG, Zhaomeng LIU, Xuanwen GAO, Wenbin LUO. Research progress and prospect of potassium ion battery electrolyte [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1409-1426. |
| [10] | Wenchao SHI, Yu LIU, Bomian ZHANG, Qi LI, Chunhua HAN, Liqiang MAI. Research progress and prospect on electrolyte additives for stabilizing the zinc anode interface in aqueous batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1589-1603. |
| [11] | Jintao LI, Yue MU, Jing WANG, Jingyi QIU, Hai MING. Investigation of the structural evolution and interface behavior in cathode materials for Li-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1636-1654. |
| [12] | Kangkang QU, Yahua LIU, Die HONG, Zhaoxi SHEN, Xiaozhao HAN, Xu ZHANG. Research progress on positive electrolytes for neutral aqueous organic redox flow battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1570-1588. |
| [13] | Lei LEI, Peng GAO, Nana FENG, Kunpeng CAI, Hai ZHANG, Yang ZHANG. The influences of multifactors in the synthesis progress on the characteristics of lithium lanthanum zirconate solid electrolytes [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1625-1635. |
| [14] | Shangzhuo LI, Yutong LONG, Zhaomeng LIU, Xuanwen GAO, Wenbin LUO. Advances toward polyanionic cathode materials for potassium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(5): 1348-1363. |
| [15] | Weibin HUANG, Biao ZHANG, Jincheng FAN, Wei YANG, Hanbo ZOU, Shengzhou CHEN. Preparation and modification of ZIF-8 composite PEO based solid electrolyte [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(4): 1083-1092. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
