Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2021, Vol. 10 ›› Issue (6): 2069-2076.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2021.0160
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yue SU1( ), Xuhua LIU1, Fanglei ZENG1,2, Yurong REN1,2, Bencai LIN1,2(
), Xuhua LIU1, Fanglei ZENG1,2, Yurong REN1,2, Bencai LIN1,2( )
)
Received:2021-04-15
Revised:2021-05-31
Online:2021-11-05
Published:2021-11-03
CLC Number:
Yue SU, Xuhua LIU, Fanglei ZENG, Yurong REN, Bencai LIN. Preparation and properties of polyvinylidene fluoride/polyvinylidene fluoride sulfonate lithium/lithium salt composite solid electrolyte[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 2069-2076.
Table 2
Tensile strength, Young's modulus and elongation at break of various SPEs"
| 样品 | 拉伸强度/MPa | 杨氏模量/MPa | 断裂伸长率/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPVDFLi-60 | 2.3±0.3 | 13.7±0.6 | 23.0±0.2 |
| SPVDFLi/LiTFSI-10 | 3.1±0.5 | 29.5±0.2 | 25.8±0.5 |
| SPVDFLi/LiTFSI-20 | 4.0±0.2 | 14.8±0.9 | 33.7±0.4 |
| SPVDFLi/LiTFSI-30 | 3.0±0.1 | 12.7±0.4 | 35.1±0.7 |
| SPVDFLi/LiTFSI-40 | 4.2±0.2 | 16.5±0.3 | 56.5±0.1 |
| PVDF/LiTFSI | 8.0±0.4 | 55.2±0.2 | 35.8±0.2 |
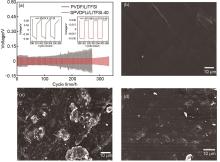
Fig. 5
Galvanostatic cycling performance of symmetric Li/SPE/Li cells with PVDF/LiTFSI and SPVDFLi/LiTFSI-40 at room temperature (a), SEM images of the surface of the fresh Li anode (b), Li anode surface after 273 h with PVDF/LiTFSI (c) and Li anode surface after 334 h with SPVDFLi/LiTFSI-40"

| 1 | 李杨, 丁飞, 桑林, 等. 全固态锂离子电池关键材料研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2016, 5(5): 615-626. |
| LI Y, DING F, SANG L, et al. A review of key materials for all-solid-state lithium ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2016, 5(5): 615-626. | |
| 2 | MILLER T F, WANG Z G, COATES G W, et al. Designing polymer electrolytes for safe and high capacity rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2017, 50(3): 590-593. |
| 3 | LYU F, WANG Z Y, SHI L Y, et al. Challenges and development of composite solid-state electrolytes for high-performance lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 441: doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.227175. |
| 4 | CHEN J, WU J W, WANG X D, et al. Research progress and application prospect of solid-state electrolytes in commercial lithium-ion power batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 35: 70-87. |
| 5 | RAMESH S, LU S C, MORRIS E. Towards magnesium ion conducting poly(vinylidenefluoride-hexafluoropropylene)-based solid polymer electrolytes with great prospects: Ionic conductivity and dielectric behaviours[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2012, 43(5): 806-812. |
| 6 | REN W H, DING C F, FU X W, et al. Advanced gel polymer electrolytes for safe and durable lithium metal batteries: Challenges, strategies, and perspectives[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 34: 515-535. |
| 7 | KNAUTH P. Inorganic solid Li ion conductors: An overview[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2009, 180(14/15/16): 911-916. |
| 8 | WANG Y, RICHARDS W D, ONG S P, et al. Design principles for solid-state lithium superionic conductors[J]. Nature Materials, 2015, 14(10): 1026-1031. |
| 9 | FENTON D E, PARKER J M, WRIGHT P V. Complexes of alkali metal ions with poly(ethylene oxide)[J]. Polymer, 1973, 14(11): doi: 10.1016/0032-3861(73)90146-8. |
| 10 | LOPEZ J, MACKANIC D G, CUI Y, et al. Designing polymers for advanced battery chemistries[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2019, 4(5): 312-330. |
| 11 | TANG S, GUO W, FU Y Z. Advances in composite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries and beyond[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(2): doi: 10.1002/aenm.202000802. |
| 12 | LIANG S W, CHEN Q, CHOI U H, et al. Plasticizing Li single-ion conductors with low-volatility siloxane copolymers and oligomers containing ethylene oxide and cyclic carbonates[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(42): 21269-21276. |
| 13 | LAGO N, GARCIA-CALVO O, LOPEZDELAMO J M, et al. All-solid-state lithium-ion batteries with grafted ceramic nanoparticles dispersed in solid polymer electrolytes[J]. ChemSusChem, 2015, 8(18): 3039-3043. |
| 14 | WANG H C, SHENG L, YASIN G, et al. Reviewing the current status and development of polymer electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 33: 188-215. |
| 15 | COSTA C M, LIZUNDIA E, LANCEROS-MÉNDEZ S. Polymers for advanced lithium-ion batteries: State of the art and future needs on polymers for the different battery components[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2020, 79: doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2020.100846. |
| 16 | MENG N, ZHANG H N, LIANLI S Y, et al. Salt-with-Salt, a novel strategy to design the flexible solid electrolyte membrane for highly safe lithium metal batteries[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020, 597: doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2019.117768. |
| 17 | MARTINEZ-IBAÑEZ M, SANCHEZ-DIEZ E, QIAO L X, et al. Unprecedented improvement of single Li-ion conductive solid polymer electrolyte through salt additive[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(16): doi: 10.1002/adfm.202000455. |
| 18 | 周井. 含超级离域磺酰亚胺阴离子锂盐的合成及其性能表征[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2018. |
| ZHOU J. Synthesis and characterization of lithium salts containing super-delocalized sulfonimides anion[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong | |
| University of Science and Technology, 2018. | |
| 19 | XUE Z G, HE D, XIE X L. Poly(ethylene oxide)-based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(38): 19218-19253. |
| 20 | RICHARDS G N. Ion-exchange membranes by sulfonation of poly(vinylidene fluoride) films[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 1964, 8(5): 2269-2280. |
| 21 | FARROKHZAD H, KIKHAVANI T, MONNAIE F, et al. Novel composite cation exchange films based on sulfonated PVDF for electromembrane separations[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 474: 167-174. |
| 22 | LU N, ZHANG X, NA R Q, et al. High performance electrospun Li+-functionalized sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone)/PVA based nanocomposite gel polymer electrolyte for solid-state electric double layer capacitors[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019, 534: 672-682. |
| 23 | SHI X J, MA N Y, WU Y X, et al. Fabrication and electrochemical properties of LATP/PVDF composite electrolytes for rechargeable lithium-ion battery[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2018, 325: 112-119. |
| [1] | LI Yitao, SHEN Kaier, PANG Quanquan. Advance in organics enhanced sulfide-based solid-state batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1902-1918. |
| [2] | Chaochao WEI, Chuang YU, Zhongkai WU, Linfeng PENG, Shijie CHENG, Jia XIE. Research progress of Li3PS4 solid electrolyte [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1368-1382. |
| [3] | Liangtao XIONG, Jifen WANG, Huaqing XIE, Xuelai ZHANG. Effect of vacancy defects on thermal conductivity of single-layer graphene by molecular dynamics [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1322-1330. |
| [4] | Zhuo XU, Lili ZHENG, Bing CHEN, Tao ZHANG, Xiuling CHANG, Shouli WEI, Zuoqiang DAI. Overview of research on composite electrolytes for solid-state batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(6): 2117-2126. |
| [5] | Bohui LU, Zhicheng SHI, Yongxue ZHANG, Hongyu ZHAO, Zixi WANG. Investigation of the charging and discharging performance of paraffin/nano-Fe3O4 composite phase change material in a shell and tube thermal energy storage unit [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(5): 1709-1719. |
| [6] | Yanfang ZHAI, Guanming YANG, Wangshu HOU, Jianyao YAO, Zhaoyin WEN, Shufeng SONG, Ning HU. Solvothermal synthesis of three-dimensional petaloid garnet electrolyte and its application in solid polymer electrolytes [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(3): 905-913. |
| [7] | Xie WU, Li ZHOU, Zhaoming XUE. Synthesis and performance of solid polymer electrolytes based on chelated boron lithium salts [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(1): 96-103. |
| [8] | Hang TU, Hang ZHANG, Lihui LIU, Jie LI, Xiaoqin SUN. Study on heat transfer of phase change materials imbedded in a concrete wall [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(1): 287-294. |
| [9] | Youman ZHAO, Xiaobo YAN, Hongkun DUAN, Zewei CHEN. Exploring mechanism of carbon nanotubes as conductive agent for improving performance of a silicon/carbon anode in LIB [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(1): 118-127. |
| [10] | Manman JIA, Long ZHANG. Recent development on sulfide solid electrolytes for solid-state sodium batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(5): 1266-1283. |
| [11] | Ge SUN, Zhixuan WEI, Xinyuan ZHANG, Nan CHEN, Gang CHEN, Fei DU. Recent progress of sodium-based inorganic solid electrolytes [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(5): 1251-1265. |
| [12] | Jie WU, Xiaobiao JIANG, Yang YANG, Yongmin WU, Lei ZHU, Weiping TANG. Progress of NASICON-structured Li1+xAlxTi2-x(PO4)3 (0 ≤x≤ 0.5) solid electrolyte [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(5): 1472-1488. |
| [13] | Jing YANG, Gaozhan LIU, Lin SHEN, Xiayin YAO. Research progress on NASICON-structured sodium solid electrolytes and their derived solid state sodium batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(5): 1284-1299. |
| [14] | Linfeng PENG, Huanhuan JIA, Qing DING, Yuming ZHAO, Jia XIE, Shijie CHENG. Research progress of solid-state sodium batteries using inorganic sodium ion conductors [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(5): 1370-1382. |
| [15] | QU Chenying, HOU Zhaoxia, WANG Xiaohui, WANG Jian, WANG Kai, LI Siyao. Research progress of gel polymer electrolytes on solid supercapacitors [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(3): 776-783. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
