Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (8): 2519-2528.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.0236
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Chaofeng XU1,2( ), Xiaolei HAN1,2, Jinzhi WANG2,3,4, Xiaojun WANG1(
), Xiaolei HAN1,2, Jinzhi WANG2,3,4, Xiaojun WANG1( ), Zhiming LIU1(
), Zhiming LIU1( ), Jingwen ZHAO2,3,4(
), Jingwen ZHAO2,3,4( )
)
Received:2024-03-18
Revised:2024-04-16
Online:2024-08-28
Published:2024-08-15
Contact:
Xiaojun WANG, Zhiming LIU, Jingwen ZHAO
E-mail:xucf@qibebt.ac.cn;wangxiaojunchem@163.com;zmliu@qust.edu.cn;zhaojw@qibebt.ac.cn
CLC Number:
Chaofeng XU, Xiaolei HAN, Jinzhi WANG, Xiaojun WANG, Zhiming LIU, Jingwen ZHAO. Crystalline zinc-ion solid-state electrolytes based on weak coordination environments[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(8): 2519-2528.
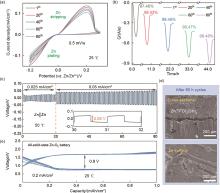
Fig. 5
(a) Cyclic voltammetry (CV) curves and (b) corresponding chronocoulometry curves of Zn plating/stripping using Zn|Zn(TFO)2(SN)4|Ti cells; (c) Plating/stripping test of the Zn||Zn symmetric cell with Zn(TFO)2(SN)4 at 0.05 mA/cm2; (d) Cross-sectional and surface SEM images of zinc electrodes after 80 h cycling in Zn(TFO)2(SN)4; (e) Charge-discharge profiles of the all-solid-state Zn-O2 cell"
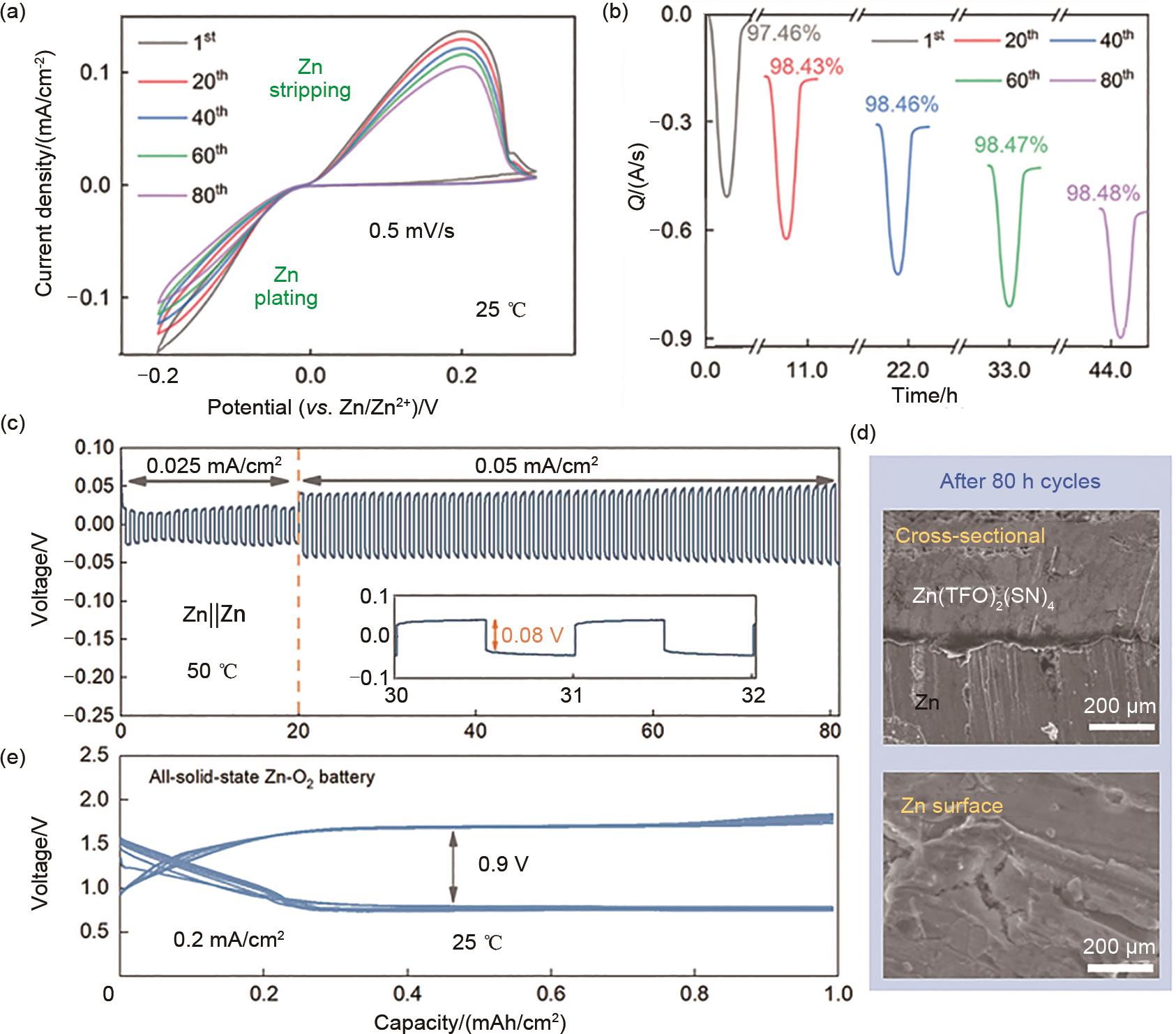
Table 1
Comparison of the performance of Zn(TFO)2(SN)4 solid state electrolyte with other types of solid state electrolytes"
| 锌离子固态电解质 | 离子电导率 /(S/cm) | 电流密度/(mA/cm2)/极化电压/V | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zn(TFO)2(SN)4 | 4.4×10-6(RT) | 0.05/0.08 | 本工作 |
| PVHF-Zn(TFO)2 | 1.99×10-6(RT) | 0.2/0.4(寿命<40 h) | [ |
| PEO-Zn(TFO)2 | 1.09×10-6(RT) | — | [ |
| ZnCl2(PEO)24 | 10-9~10-8(RT) | — | [ |
| ZnX2(PEO)20(X=Br, I) | 10-9~10-8(RT) | — | [ |
| ZnCl2PEO n (n=4~16) | 10-8~10-7(RT) | — | [ |
| 1 | MA T H, WANG Z X, WU D X, et al. High-areal-capacity and long-cycle-life all-solid-state battery enabled by freeze drying technology[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2023, 16(5): 2142-2152. DOI: 10.1039/D3EE00420A. |
| 2 | LIU W, ZHAO Q W, YU H M, et al. Metallic particles-induced surface reconstruction enabling highly durable zinc metal anode[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(38): 2302661. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202302661. |
| 3 | PARKER J F, CHERVIN C N, PALA I R, et al. Rechargeable nickel-3D zinc batteries: An energy-dense, safer alternative to lithium-ion[J]. Science, 2017, 356(6336): 415-418. DOI: 10.1126/science.aak9991. |
| 4 | ZHENG J X, ZHAO Q, TANG T, et al. Reversible epitaxial electrodeposition of metals in battery anodes[J]. Science, 2019, 366(6465): 645-648. DOI: 10.1126/science.aax6873. |
| 5 | SHEN Y H, LIU B, LIU X R, et al. Water-in-salt electrolyte for safe and high-energy aqueous battery[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 34: 461-474. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2020.10.011. |
| 6 | ZHANG L, RODRÍGUEZ-PÉREZ I A, JIANG H, et al. ZnCl2 "water-in-salt" electrolyte transforms the performance of vanadium oxide as a Zn battery cathode[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(30): 1902653. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201902653. |
| 7 | SUN L, YAO Y Q, DAI L X, et al. Sustainable and high-performance Zn dual-ion batteries with a hydrogel-based water-in-salt electrolyte[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 47: 187-194. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2022.02.012. |
| 8 | ZHANG Y N, WU D S, HUANG F L, et al. "Water-in-salt" nonalkaline gel polymer electrolytes enable flexible zinc-air batteries with ultra-long operating time[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(34): 2203204. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202203204. |
| 9 | WANG J, TIAN J X, LIU G X, et al. In situ insight into the interfacial dynamics in "water-in-salt" electrolyte-based aqueous zinc batteries[J]. Small Methods, 2023, 7(6): 2300392. DOI: 10.1002/smtd.202300392. |
| 10 | DI S L, NIE X Y, MA G Q, et al. Zinc anode stabilized by an organic-inorganic hybrid solid electrolyte interphase[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 43: 375-382. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm. 2021.09.021. |
| 11 | CHEN J Z, ZHOU W J, QUAN Y H, et al. Ionic liquid additive enabling anti-freezing aqueous electrolyte and dendrite-free Zn metal electrode with organic/inorganic hybrid solid electrolyte interphase layer[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 53: 629-637. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2022.10.004. |
| 12 | HOU Z G, ZHANG X Q, DONG M F, et al. A large format aqueous rechargeable LiMn2O4/Zn battery with high energy density and long cycle life[J]. Science China Materials, 2021, 64(3): 783-788. DOI: 10.1007/s40843-020-1503-7. |
| 13 | KUNDU D P, HOSSEINI VAJARGAH S, WAN L W, et al. Aqueous vs. nonaqueous Zn-ion batteries: Consequences of the desolvation penalty at the interface[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(4): 881-892. DOI: 10.1039/C8EE00378E. |
| 14 | WANG F, BORODIN O, GAO T, et al. Highly reversible zinc metal anode for aqueous batteries[J]. Nature Materials, 2018, 17: 543-549. DOI: 10.1038/s41563-018-0063-z. |
| 15 | KANG L Z, ZHENG J L, YUE K, et al. Amino-functionalized interfacial layer enables an ultra-uniform amorphous solid electrolyte interphase for high-performance aqueous zinc-based batteries[J]. Small, 2023, 19(44): DOI: 10.1002/smll.202304094. |
| 16 | LIN Y X, LI Y, MAI Z X, et al. Interfacial regulation via anionic surfactant electrolyte additive promotes stable (002)-textured zinc anodes at high depth of discharge[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(38): 2301999. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202301999. |
| 17 | AN Y L, XU B G, TIAN Y, et al. Reversible Zn electrodeposition enabled by interfacial chemistry manipulation for high-energy anode-free Zn batteries[J]. Materials Today, 2023, 70: 93-103. DOI: 10.1016/j.mattod.2023.09.008. |
| 18 | XIE S Y, LI Y, DONG L B. Stable anode-free zinc-ion batteries enabled by alloy network-modulated zinc deposition interface[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2023, 76: 32-40. DOI: 10.1016/j.jechem.2022.08.040. |
| 19 | CAO L S, LI D, HU E Y, et al. Solvation structure design for aqueous Zn metal batteries[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(51): 21404-21409. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.0c09794. |
| 20 | ZHENG J X, ARCHER L A. Controlling electrochemical growth of metallic zinc electrodes: Toward affordable rechargeable energy storage systems[J]. Science Advances, 2021, 7(2): eabe0219. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abe0219. |
| 21 | DUERAMAE I, OKHAWILAI M, KASEMSIRI P, et al. Properties enhancement of carboxymethyl cellulose with thermo-responsive polymer as solid polymer electrolyte for zinc ion battery[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 12587. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-69521-x. |
| 22 | YANG P H, FENG C Z, LIU Y P, et al. Thermal self-protection of zinc-ion batteries enabled by smart hygroscopic hydrogel electrolytes[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(48): 2002898. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202002898. |
| 23 | ZHU J C, YAO M J, HUANG S, et al. Thermal-gated polymer electrolytes for smart zinc-ion batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(38): 16480-16484. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202007274. |
| 24 | LIU Y, ZOU H Q, HUANG Z L, et al. In situ polymerization of 1, 3-dioxane as a highly compatible polymer electrolyte to enable the stable operation of 4.5 V Li-metal batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2023, 16(12): 6110-6119. DOI: 10.1039/D3EE02797J. |
| 25 | LI J C, MA C, CHI M F, et al. Solid electrolyte: The key for high-voltage lithium batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2015, 5(4): 1401408. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201401408. |
| 26 | BAN A H, PARK M S, PARK T H, et al. Nonflammable ionic liquid-based quasi-solid-state electrolytes for highly safe sodium-ion batteries[J]. ECS Meeting Abstracts, 2021, (6): 405. DOI: 10. 1149/ma2021-016405mtgabs. |
| 27 | LI Y S, YANG X D, HE Y, et al. A novel ultrathin multiple-kinetics-enhanced polymer electrolyte editing enabled wide-temperature fast-charging solid-state zinc metal batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(4): 2307736. DOI: 10.1002/adfm. 202307736. |
| 28 | QIU B, LIANG K Y, HUANG W, et al. Crystal-facet manipulation and interface regulation via TMP-modulated solid polymer electrolytes toward high-performance Zn metal batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(32): 2301193. DOI: 10. 1002/aenm.202301193. |
| 29 | 黄渭彬, 张彪, 范金成, 等. ZIF-8复合PEO基固态电解质的制备与改性研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(4): 1083-1092. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2022.0532. |
| HUANG W B, ZHANG B, FAN J C, et al. Preparation and modification of ZIF-8 composite PEO based solid electrolyte[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(4): 1083-1092. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2022.0532. | |
| 30 | IMANAKA N, TAMURA S. Development of multivalent ion conducting solid electrolytes[J]. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 2011, 84(4): 353-362. DOI: 10.1246/bcsj.20100178. |
| 31 | IKEDA S, KANBAYASHI Y, NOMURA K, et al. Solid electrolytes with multivalent cation conduction (2): Zinc ion conduction in Zn-Zr-PO4 system[J]. Solid State Ionics, 1990, 40: 79-82. DOI: 10.1016/0167-2738(90)90291-X. |
| 32 | JOHNSON D A, NELSON P G. Factors determining the ligand field stabilization energies of the hexaaqua 2+ complexes of the first transition series and the Irving-williams order[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 1995, 34(22): 5666-5671. DOI: 10.1021/ic00126a041. |
| 33 | HOU Z G, DONG M F, XIONG Y L, et al. A high-energy and long-life aqueous Zn/birnessite battery via reversible water and Zn2+ coinsertion[J]. Small, 2020, 16(26): e2001228. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202001228. |
| 34 | RICHENS D T. Ligand substitution reactions at inorganic centers[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2005, 105(6): 1961-2002. DOI: 10.1021/cr030705u. |
| 35 | PRAKASH P, FALL B, AGUIRRE J, et al. A soft co-crystalline solid electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Nature Materials, 2023, 22(5): 627-635. DOI: 10.1038/s41563-023-01508-1. |
| 36 | WANG J, ZHAO Z, LU G, et al. Room-temperature fast zinc-ion conduction in molecule-flexible solids[J]. Materials Today Energy, 2021, 20: 100630. DOI: 10.1016/j.mtener.2020.100630. |
| 37 | ALARCO P J, ABU-LEBDEH Y, ABOUIMRANE A, et al. The plastic-crystalline phase of succinonitrile as a universal matrix for solid-state ionic conductors[J]. Nature Materials, 2004, 3: 476-481. DOI: 10.1038/nmat1158. |
| 38 | GOODENOUGH J B, HONG H Y P, KAFALAS J A. Fast Na+-ion transport in skeleton structures[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 1976, 11(2): 203-220. DOI: 10.1016/0025-5408(76)90077-5. |
| 39 | HONG H Y P. Crystal structures and crystal chemistry in the system Na1+ xZr2SixP3- xO12[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 1976, 11(2): 173-182. DOI: 10.1016/0025-5408(76)90073-8. |
| 40 | DINNEBIER R, SOFINA N, HILDEBRANDT L, et al. Crystal structures of the trifluoromethyl sulfonates M(SO3CF3)2 (M=Mg, Ca, Ba, Zn, Cu) from synchrotron X-ray powder diffraction data[J]. Acta Crystallographica Section B, Structural Science, 2006, 62(Pt 3): 467-473. DOI: 10.1107/S0108768106009517. |
| 41 | MANTHIRAM A, GOODENOUGH J B. Layered lithium cobalt oxide cathodes[J]. Nature Energy, 2021, 6: 323. DOI: 10.1038/s41560-020-00764-8. |
| 42 | ROEDERN E, KÜHNEL R S, REMHOF A, et al. Magnesium ethylenediamine borohydride as solid-state electrolyte for magnesium batteries[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 46189. DOI: 10.1038/srep 46189. |
| 43 | IMANAKA N, TAMURA S. Development of multivalent ion conducting solid electrolytes[J]. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 2011, 84(4): 353-362. DOI: 10.1246/bcsj.20100178. |
| 44 | SHEN Y N, DENG G H, GE C Q, et al. Solvation structure around the Li+ ion in succinonitrile-lithium salt plastic crystalline electrolytes[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2016, 18(22): 14867-14873. DOI: 10.1039/C6CP02878K. |
| 45 | UMAR Y, MORSY M A. Ab initio and DFT studies of the molecular structures and vibrational spectra of succinonitrile[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2007, 66(4/5): 1133-1140. DOI: 10.1016/j.saa. 2006.05.026. |
| 46 | DAIGLE J C, ARNOLD A, VIJH A, et al. Solid-state NMR study of new copolymers as solid polymer electrolytes[J]. Magnetochemistry, 2018, 4(1): 13. DOI: 10.3390/magnetochemistry4010013. |
| 47 | FREITAG K M, KIRCHHAIN H, VAN WÜLLEN L, et al. Enhancement of Li ion conductivity by electrospun polymer fibers and direct fabrication of solvent-free separator membranes for Li ion batteries[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2017, 56(4): 2100-2107. DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.6b02781. |
| 48 | BOTTKE P, RETTENWANDER D, SCHMIDT W, et al. Ion dynamics in solid electrolytes: NMR reveals the elementary steps of Li+ hopping in the garnet Li6.5La3Zr1.75Mo0.25O12[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2015, 27(19): 6571-6582. DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b02231. |
| 49 | YANG H, HUQ R, FARRINGTON G C. Conductivity in PEO-based Zn(II) polymer electrolytes[J]. Solid State Ionics, 1990, 40: 663-665. DOI: 10.1016/0167-2738(90)90093-7. |
| 50 | VIJAYAKUMAR V, GHOSH M, KURIAN M, et al. An in situ cross-linked nonaqueous polymer electrolyte for zinc-metal polymer batteries and hybrid supercapacitors[J]. Small, 2020, 16(35): e2002528. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202002528. |
| 51 | ZENG Z Q, LIU G Z, JIANG Z P, et al. Zinc bis(2-ethylhexanoate), a homogeneous and bifunctional additive, to improve conductivity and lithium deposition for poly (ethylene oxide) based all-solid-state lithium metal battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 451: 227730. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2020.227730. |
| 52 | KARAN S, SAHU T B, SAHU M, et al. Characterization of ion transport property in hot-press cast solid polymer electrolyte (SPE) films: [PEO: Zn(CF3SO3)2][J]. Ionics, 2017, 23(10): 2721-2726. DOI: 10.1007/s11581-017-2036-7. |
| 53 | OVERBURY S H, BERTRAND P A, SOMORJAI G A. Surface composition of binary systems. Prediction of surface phase diagrams of solid solutions[J]. Chemical Reviews, 1975, 75(5): 547-560. DOI: 10.1021/cr60297a001. |
| 54 | BRUNO M. A revised thermodynamic model for crystal surfaces. I. Theoretical aspects[J]. CrystEngComm, 2017, 19(42): 6314-6324. DOI: 10.1039/C7CE01397C. |
| 55 | CHEN Z, LI X L, WANG D H, et al. Grafted MXene/polymer electrolyte for high performance solid zinc batteries with enhanced shelf life at low/high temperatures[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(6): 3492-3501. DOI: 10.1039/D1EE00409C. |
| 56 | PLANCHA M J C, RANGEL C M, SEQUEIRA C A C. Pseudo-equilibrium phase diagrams for PEO-Zn salts-based electrolytes[J]. Solid State Ionics, 1999, 116(3/4): 293-300. DOI: 10.1016/S0167-2738(98)00356-7. |
| 57 | YANG H, FARRINGTON G C. Poly(ethylene oxide)-based Zn(II) halide electrolytes[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1992, 139(6): 1646-1654. DOI: 10.1149/1.2069471. |
| [1] | Ye CHEN, Jin LI, Houfu WU, Shaoyu ZHANG, Yuxi CHU, Ping ZHUO. Analysis of thermal runaway propagation and explosion risk of a large battery module for energy storage [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(8): 2803-2812. |
| [2] | Yufeng HUANG, Huanchao LIANG, Lei XU. Kalman filter optimize Transformer method for state of health prediction on lithium-ion battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(8): 2791-2802. |
| [3] | Yanyan KONG, Xiong ZHANG, Yabin AN, Chen LI, Xianzhong SUN, Kai WANG, Yanwei MA. Recent advances in preparation of MOF-derived porous carbon-based materials and their applications in anodes of lithium-ion capacitors [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(8): 2665-2678. |
| [4] | Yuan YAO, Ruoqi ZONG, Jianli GAI. Research progress of antimony- and bismuth-based metallic anode materials for sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(8): 2649-2664. |
| [5] | Wenhao GONG, Meng LI, Tao ZHANG, Ruotao ZHANG, Yanxia LIU. Development and fabrication of high-energy and long-endurance Li-ion batteries for UAVs [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(8): 2550-2558. |
| [6] | Lijun FAN, Baozhou WU, Kejun CHEN. Controllable synthesis of FeS2 with different morphologies and their sodium storage performances [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(8): 2541-2549. |
| [7] | Jieyu ZHANG, Shun ZHANG, Ning LI, Fanglei ZENG, Jianning DING. Preparation and performance of a flame-retardant gel polymer electrolyte [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(8): 2529-2540. |
| [8] | Chenqiang DU, Zhouhuan NIE, Huinan WANG, Jiwei ZHANG, Jingwei ZHANG. Construction of built-in electric field in TiO2@TiN heterojunctions toward boosting the polysulfide conversion [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(8): 2499-2510. |
| [9] | Dingbang HAO, Yongli LI. Na0.85Ni0.3Fe0.2Mn0.5O1.95F0.05@CuO cathode materials for high-rate and long cycling stability sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(8): 2489-2498. |
| [10] | Zhiyong WANG, Junyao CAI, Yingqi SHE, Shulin ZHONG, Kanghua PAN. Surface-modification of graphite with N-heterocyclic conducting polymers as high performance anodes for Li-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(8): 2511-2518. |
| [11] | Xiaojun ZHAO, Yingchao WANG, Meng CHEN, Peng YANG, Zhanwang AN, Jianli LIU, Di WU. Reliability analysis of the module busbars of power battery systems [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2450-2458. |
| [12] | Sen JIANG, Long CHEN, Chuangchao SUN, Jinze WANG, Ruhong LI, Xiulin FAN. Low-temperature lithium battery electrolytes: Progress and perspectives [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2270-2285. |
| [13] | Xiaoyu CHEN, Yu LIU, Yifan BAI, Jiajun YING, Ying LV, Lijia WAN, Junping HU, Xiaoling Chen. Preparation and performance of nickel cobalt hydroxide cathode material for nickel zinc batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2377-2385. |
| [14] | Yang LU, Shuaishuai YAN, Xiao MA, Zhi LIU, Weili ZHANG, Kai LIU. Low-temperature electrolytes and their application in lithium batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2224-2242. |
| [15] | Shijie LIAO, Ying WEI, Yunhui HUANG, Renzong HU, Henghui XU. 1,3-Difluorobenzene diluent-stabilizing electrode interface for high-performance low-temperature lithium metal batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2124-2130. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
