Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (8): 3207-3215.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2025.0120
• Energy Storage Test: Methods and Evaluation • Previous Articles
Chao PANG1,2( ), Shuang DING2, Xiaokun ZHANG1(
), Shuang DING2, Xiaokun ZHANG1( ), Yong XIANG1
), Yong XIANG1
Received:2025-02-12
Revised:2025-02-24
Online:2025-08-28
Published:2025-08-18
Contact:
Xiaokun ZHANG
E-mail:pc11qdu@163.com;zxk@uestc.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Chao PANG, Shuang DING, Xiaokun ZHANG, Yong XIANG. Simulation study of the solvation structure and ion migration behavior in localized high-concentration electrolytes[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(8): 3207-3215.
Table 1
Initial molecular numbers of LiFSI, DME, and D2 in different simulation systems"
| 项目 | 体系(摩尔比) | 缩写 | LiFSI | DME | D2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCE | LiFSI-9DME | LCE | 60 | 540 | — |
| HCE | LiFSI-1.2DME | HCE1 | 200 | 240 | — |
| LiFSI-1.5DME | HCE2 | 186 | 279 | — | |
| LHCE | LiFSI-1.2DME-D2 | LHCE1 | 115 | 138 | 115 |
| LiFSI-1.5DME-D2 | LHCE2 | 110 | 165 | 110 | |
| LiFSI-1.2DME-2D2 | LHCE3 | 80 | 96 | 160 | |
| LiFSI-1.5DME-2D2 | LHCE4 | 78 | 118 | 156 | |
| LiFSI-1.2DME-6D2 | LHCE5 | 35 | 42 | 210 | |
| LiFSI-1.5DME-6D2 | LHCE6 | 32 | 48 | 192 | |
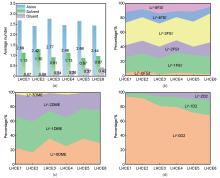
Fig. 2
Analysis of Li+ solvation structures in six LHCE systems: LHCE1/3/5: LiFSI-1.2DME-xD2; LHCE2/4/6: LiFSI-1.5DME-xD2 (diluent molar ratio x=1, 2, 6). (a) Average coordination numbers of Li+ with anions (FSI-), solvent (DME), and diluent (D2); (b) Probability distribution of Li+-FSI-coordination numbers; (c) Probability distribution of Li+-DME coordination numbers; (d) Probability distribution of Li+-D2 coordination interactions"
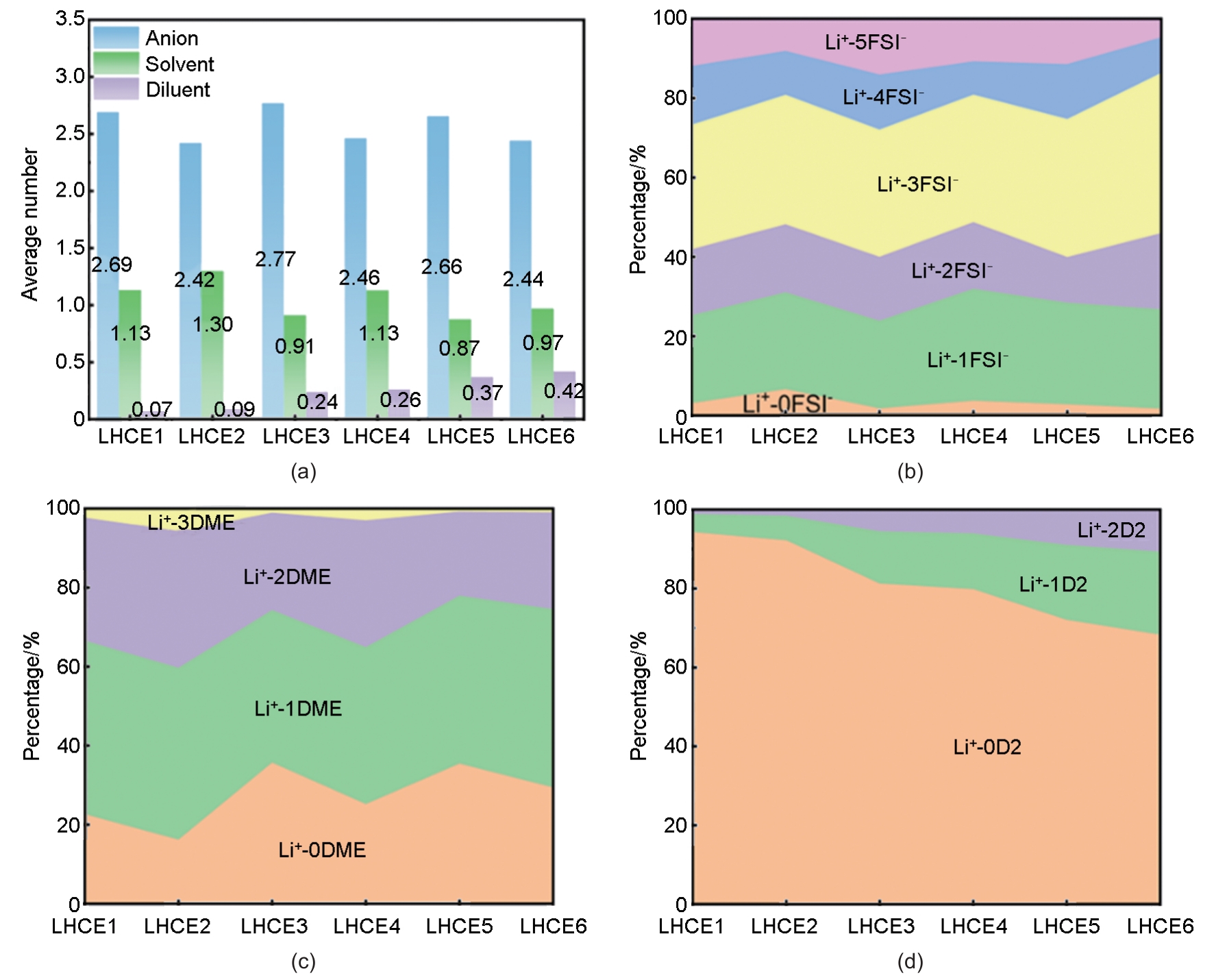
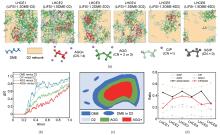
Fig. 3
MD simulations of LHCE systems with varied compositions: LHCE1/3/5: LiFSI-1.2DME-xD2; LHCE2/4/6: LiFSI-1.5DME-xD2 (diluent molar ratio x=1, 2, 6). (a) Snapshots of spatial distributions for cluster types (SSIP, CIP, AGG, AGG+) and DME molecules; (b) RDFs of DME-D2, CIP-D2, AGG-D2, and AGG+-D2 pairs; (c) Schematic spatial partitioning: blue (Li+-DME coordination), green (AGG clusters), red (AGG+ clusters), with free DME (blue ellipse) in the D2 diluent phase; (d) Ratios of SSIP, CIP, AGG, AGG+ clusters and CIP/AGG, AGG+/AGG transitions"
| [1] | 陆洋, 闫帅帅, 马骁, 等. 低温锂电池电解液的研究与应用[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(7): 2224-2242. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239. 2024.0313. |
| LU Y, YAN S S, MA X, et al. Low-temperature electrolytes and their application in lithium batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2224-2242. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.0313. | |
| [2] | DIEDERICHSEN K M, MCSHANE E J, MCCLOSKEY B D. Promising routes to a high Li+ transference number electrolyte for lithium ion batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2017, 2(11): 2563-2575. DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.7b00792. |
| [3] | ZHOU P, ZHANG X K, XIANG Y, et al. Strategies to enhance Li+ transference number in liquid electrolytes for better lithium batteries[J]. Nano Research, 2023, 16(6): 8055-8071. DOI: 10. 1007/s12274-022-4833-1. |
| [4] | YAO N, YU L G, FU Z H, et al. Probing the origin of viscosity of liquid electrolytes for lithium batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(41): e202305331. DOI: 10.1002/anie. 202305331. |
| [5] | CHEN J E, ZHANG H, FANG M M, et al. Design of localized high-concentration electrolytes via donor number[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2023, 8(4): 1723-1734. DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.3c00004. |
| [6] | REN F H, LI Z D, CHEN J H, et al. Solvent-diluent interaction-mediated solvation structure of localized high-concentration electrolytes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(3): 4211-4219. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.1c21638. |
| [7] | PARK E, PARK J, LEE K, et al. Exploiting the steric effect and low dielectric constant of 1,2-dimethoxypropane for 4.3 V lithium metal batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2023, 8(1): 179-188. |
| [8] | HOSSAIN M J, WU Q S, MARIN BERNARDEZ E J, et al. The relationship between ionic conductivity and solvation structures of localized high-concentration fluorinated electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2023, 14(34): 7718-7731. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.3c01453. |
| [9] | PEREZ BELTRAN S, CAO X, ZHANG J G, et al. Influence of diluent concentration in localized high concentration electrolytes: Elucidation of hidden diluent-Li+ interactions and Li+ transport mechanism[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(32): 17459-17473. DOI: 10.1039/D1TA04737J. |
| [10] | EFAW C M, WU Q S, GAO N, et al. Localized high-concentration electrolytes get more localized through micelle-like structures[J]. Nature Materials, 2023, 22(12): 1531-1539. DOI: 10.1038/s41563-023-01700-3. |
| [11] | CAO X, ZOU L F, MATTHEWS B E, et al. Optimization of fluorinated orthoformate based electrolytes for practical high-voltage lithium metal batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 34: 76-84. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2020.08.035. |
| [12] | LI Q, LIU G, CHENG H R, et al. Low-temperature electrolyte design for lithium-ion batteries: Prospect and challenges[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2021, 27(64): 15842-15865. DOI: 10.1002/chem.202101407. |
| [13] | CAO X, JIA H, XU W, et al. Review—Localized high-concentration electrolytes for lithium batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2021, 168(1): 010522. DOI: 10.1149/1945-7111/abd60e. |
| [14] | MARTÍNEZ L, ANDRADE R, BIRGIN E G, et al. PACKMOL: A package for building initial configurations for molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2009, 30(13): 2157-2164. DOI: 10.1002/jcc.21224. |
| [15] | BERENDSEN H J C, VAN DER SPOEL D, VAN DRUNEN R. GROMACS: A message-passing parallel molecular dynamics implementation[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 1995, 91(1/2/3): 43-56. DOI: 10.1016/0010-4655(95)00042-E. |
| [16] | DODDA L S, CABEZA DE VACA I, TIRADO-RIVES J, et al. LigParGen web server: An automatic OPLS-AA parameter generator for organic ligands[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, 45(W1): W331-W336. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx312. |
| [17] | PODGORŠEK A, SALAS G, CAMPBELL P S, et al. Influence of ionic association, transport properties, and solvation on the catalytic hydrogenation of 1,3-cyclohexadiene in ionic liquids[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2011, 115(42): 12150-12159. DOI: 10.1021/jp206619c. |
| [18] | NOSÉ S. A unified formulation of the constant temperature molecular dynamics methods[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1984, 81(1): 511-519. DOI: 10.1063/1.447334. |
| [19] | BERENDSEN H J C, POSTMA J P M, VAN GUNSTEREN W F, et al. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1984, 81(8): 3684-3690. DOI: 10.1063/1.448118. |
| [20] | HUMPHREY W, DALKE A, SCHULTEN K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics[J]. Journal of Molecular Graphics, 1996, 14(1): 33-38. DOI: 10.1016/0263-7855(96)00018-5. |
| [21] | WANG Y K, LI Z M, HOU Y P, et al. Emerging electrolytes with fluorinated solvents for rechargeable lithium-based batteries[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2023, 52(8): 2713-2763. DOI: 10. 1039/D2CS00873D. |
| [22] | YAMADA Y, WANG J H, KO S, et al. Advances and issues in developing salt-concentrated battery electrolytes[J]. Nature Energy, 2019, 4(4): 269-280. DOI: 10.1038/s41560-019-0336-z. |
| [23] | SELF J, FONG K D, PERSSON K A. Transport in superconcentrated LiPF6 and LiBF4/propylene carbonate electrolytes[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2019, 4(12): 2843-2849. |
| [24] | DOKKO K, WATANABE D, UGATA Y, et al. Direct evidence for Li ion hopping conduction in highly concentrated sulfolane-based liquid electrolytes[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2018, 122(47): 10736-10745. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b09439. |
| [25] | YAO N, CHEN X, SUN S Y, et al. Identifying the lithium bond and lithium ionic bond in electrolytes[J]. Chem, 2025, 11(1): 102254. DOI: 10.1016/j.chempr.2024.07.016. |
| [26] | 何一涛, 丁飞, 林立, 等. 电极界面浓差极化对锂金属沉积的影响[J]. 物理化学学报, 2021, 37(2): 157-163. DOI: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB202009001. |
| HE Y T, DING F, LIN L, et al. Influence of interfacial concentration polarization on lithium metal electrodeposition[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2021, 37(2): 157-163. DOI: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB202009001. |
| [1] | Fuxu XING, Qi QIN, Longkang WANG, Yubing LI, Shuaikai XU, Tangming MO. Recent advances in theoretical and computational simulations of pseudocapacitors [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(8): 3004-3018. |
| [2] | Yijie YAO, Junwei ZHANG, Yanjun ZHAO, Hongcheng LIANG, Dongni ZHAO. Effect of interfacial dynamics on low temperature performance of sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(1): 30-41. |
| [3] | Guobing ZHOU, Shenzhen XU. Progress of theoretical studies on the formation and growth mechanisms of solid electrolyte interphase at lithium metal anodes [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(9): 3150-3160. |
| [4] | Yang LU, Shuaishuai YAN, Xiao MA, Zhi LIU, Weili ZHANG, Kai LIU. Low-temperature electrolytes and their application in lithium batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2224-2242. |
| [5] | Chenyang ZHAO, Xiaokun YU, Yubing TAO. Preparation and characterization of modified CuO nanoparticles/n-octadecane phase change material [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(6): 1786-1793. |
| [6] | Heqing TIAN, Zhaoyang KOU, Junjie ZHOU, Yinsheng YU. Molecular dynamics simulation of structure and thermal properties of LiCl-KCl molten salt nanofluids [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(3): 654-660. |
| [7] | Huimin ZHANG, Jing WANG, Yibo WANG, Jiaxin ZHENG, Jingyi QIU, Gaoping CAO, Hao ZHANG. Multiscale modeling of the SEI of lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(2): 366-382. |
| [8] | Dianwei FU, Cancan ZHANG, Heya NA, Guoqiang WANG, Yuting WU, Yuanwei LU. Review of the molecular dynamics of molten salt thermal physical properties [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(12): 3873-3882. |
| [9] | Liangtao XIONG, Jifen WANG, Huaqing XIE, Xuelai ZHANG. Effect of vacancy defects on thermal conductivity of single-layer graphene by molecular dynamics [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(5): 1322-1330. |
| [10] | Peiping YU, Liang XU, Bingyun MA, Qintao SUN, Hao YANG, Yue LIU, Tao CHENG. Multiscale simulation of a solid electrolyte interphase [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(3): 921-928. |
| [11] | Min'an YANG, Ning CHEN, Bo WANG, Qian ZHANG, Jingpei CHEN, Hailei ZHAO, Fushen LI. Gene law about cycle stability of cathode material for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(2): 462-469. |
| [12] | ZHANG Xuelai, WANG Xuzhe, WANG Jifen, XU Xiaofeng, HUA Weisan, FANG Manting. Molecular dynamics simulation of phase transformation process of n-tetradecane [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(5): 874-879. |
| [13] | YU Jiapeng, CHENG Xiaomin, LI Yuanyuan, LI Bei, XU Hong. Molecular dynamics simulation of thermodynamic properties of Mg-Cu alloys [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(4): 772-777. |
| [14] | CHEN Bingbing, ZHAO Jinwen, MA Jun, CUI Guanglei. Relationship of ion transport and pressure in PEO/LITFSI solid electrolytes [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2018, 7(3): 431-436. |
| [15] | NI Haiou, SUN Ze, LU Guimin, YU Jianguo. Molecular dynamics simulation of structure and physical properties of NaNO3-KNO3-NaNO2 ternary phase-change molten salts [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2017, 6(4): 669-674. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
