储能科学与技术 ›› 2024, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (2): 462-479.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0614
收稿日期:2023-09-11
修回日期:2023-09-28
出版日期:2024-02-28
发布日期:2024-03-01
通讯作者:
邹才能,唐永炳
E-mail:guo@siat.ac.cn;zcn@petrochina.com.cn;tangyb@siat.ac.cn
作者简介:郭秀丽(1992—),女,博士研究生,研究方向为水系二次电池的电极材料研发,E-mail:xl. guo@siat.ac.cn;
基金资助:
Xiuli GUO1( ), Xiaolong ZHOU1, Caineng ZOU2(
), Xiaolong ZHOU1, Caineng ZOU2( ), Yongbing TANG1(
), Yongbing TANG1( )
)
Received:2023-09-11
Revised:2023-09-28
Online:2024-02-28
Published:2024-03-01
Contact:
Caineng ZOU, Yongbing TANG
E-mail:guo@siat.ac.cn;zcn@petrochina.com.cn;tangyb@siat.ac.cn
摘要:
随着消费电子、电动汽车与规模储能产业的迅速发展,人们对电化学储能技术的安全高效提出了更高的要求。然而,锂离子电池(LIBs)存在的安全隐患问题制约了其在规模储能市场的应用。水系双离子电池(ADIBs)是一类以水系电解液作为离子传输介质且阴、阳离子均作为载流子同时参与电极电化学反应的新型储能技术,具有安全性能优异、功率密度高、绿色环保、性价比高等优势,在大规模储能领域具有潜在的应用前景。本综述从ADIBs的基本工作原理以及限制其发展的关键科学问题出发,归纳了近年来从电解液设计角度出发,拓宽电化学稳定电压窗口的几种常用方法,并总结了在正极和负极材料优化、储能机理研究方面取得的重要进展。最后,基于对ADIBs的理解,对其研究前景和未来研究方向进行了展望。本文将为水系储能电池研究的工作者提供参考,并为推动ADIBs的发展和促进高安全储能技术的进步发挥积极作用。
中图分类号:
郭秀丽, 周小龙, 邹才能, 唐永炳. 水系双离子电池的研究进展与展望[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(2): 462-479.
Xiuli GUO, Xiaolong ZHOU, Caineng ZOU, Yongbing TANG. Research progress and perspectives of aqueous dual-ions batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(2): 462-479.
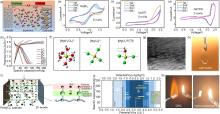
图3
(a) 使用KS6 和AC在LiFSI-LiTFSI“双盐包水”电解液中构建的ADIBs示意图[27];(b)~(d)扫速为5?mV/s时,PTCDI-G电极在含有NaBF4 、NaOTf和NaTFSI电解液中的CV曲线[29];(e) Zn||石墨电池在100~5000 mA/g(1~50 C)电流密度下对应的充放电曲线[28];(f) [Mg(H2O)6]2+ 、[MgCl4]2-和[MgCl3(H2O)]-的拉曼模型(黄色:Mg,红色:O,绿色:Cl)[33];(g) 石墨正极充电后的TEM图[33];(h) 含有25 mol/L ZnCl2 、25 mol/L ZnBr2 和25 mol/L Zn(OAc)2 的水系电解液照片[39];(i) Zn||PANI ADIBs中ZIS-PVA水凝胶电解质的示意图[41];(j) 活性材料用于水系LIBs(白色)和ADIBs(黄色)的氧化还原电位(0 V vs. Ag/AgCl,相当于3.24 V vs. Li/Li+)以及在水系电解液中的电化学稳定窗口对应的实际容量示意图[42];(k) 水系/有机系杂化电解液的燃烧试验图[43]"
| 1 | LI W J, YU X Z, HU N, et al. Study on the relationship between fossil energy consumption and carbon emission in Sichuan Province[J]. Energy Reports, 2022, 8: 53-62. |
| 2 | LARCHER D, TARASCON J M. Towards greener and more sustainable batteries for electrical energy storage[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2015, 7: 19-29. |
| 3 | DUAN J, TANG X, DAI H F, et al. Building safe lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles: A review[J]. Electrochemical Energy Reviews, 2020, 3(1): 1-42. |
| 4 | ZENG X L, LI J H, LIU L L. Solving spent lithium-ion battery problems in China: Opportunities and challenges[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2015, 52: 1759-1767. |
| 5 | JU Z N, ZHAO Q, CHAO D L, et al. Energetic aqueous batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(27): 2201074. |
| 6 | ZHANG H, LIU X, QIN B S, et al. Electrochemical intercalation of anions in graphite for high-voltage aqueous zinc battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 449: 227594. |
| 7 | OU X W, GONG D C, HAN C J, et al. Advances and prospects of dual-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(46): 2102498. |
| 8 | WU X Y, XU Y K, ZHANG C, et al. Reverse dual-ion battery via a ZnCl2 water-in-salt electrolyte[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(15): 6338-6344. |
| 9 | CHEN Y Q, KANG Y Q, ZHAO Y, et al. A review of lithium-ion battery safety concerns: The issues, strategies, and testing standards[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 59: 83-99. |
| 10 | WANG Q S, JIANG L H, YU Y, et al. Progress of enhancing the safety of lithium ion battery from the electrolyte aspect[J]. Nano Energy, 2019, 55: 93-114. |
| 11 | ZHANG H, LIU X, LI H H, et al. Challenges and strategies for high-energy aqueous electrolyte rechargeable batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2021, 60(2): 598-616. |
| 12 | CHEN C, LEE C S, TANG Y B. Fundamental understanding and optimization strategies for dual-ion batteries: A review[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2023, 15(1): 121. |
| 13 | KIM H, HONG J, PARK K Y, et al. Aqueous rechargeable Li and Na ion batteries[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(23): 11788-11827. |
| 14 | PLACKE T, HECKMANN A, SCHMUCH R, et al. Perspective on performance, cost, and technical challenges for practical dual-ion batteries[J]. Joule, 2018, 2(12): 2528-2550. |
| 15 | CHAO D L, ZHOU W H, XIE F X, et al. Roadmap for advanced aqueous batteries: From design of materials to applications[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(21): eaba4098. |
| 16 | LIU J L, XU C H, CHEN Z, et al. Progress in aqueous rechargeable batteries[J]. Green Energy & Environment, 2018, 3(1): 20-41. |
| 17 | EFTEKHARI A. High-energy aqueous lithium batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(24): 1801156. |
| 18 | ZHANG H, GUO G L, ADENUSI H, et al. Advances and issues in developing intercalation graphite cathodes for aqueous batteries[J]. Materials Today, 2022, 53: 162-172. |
| 19 | WANG S F, GUAN Y, GAN F Q, et al. Charge carriers for aqueous dual-ion batteries[J]. ChemSusChem, 2023, 16(4): e202201373. |
| 20 | BORODIN O, SELF J, PERSSON K A, et al. Uncharted waters: Super-concentrated electrolytes[J]. Joule, 2020, 4(1): 69-100. |
| 21 | SUO L M, BORODIN O, GAO T, et al. "Water-in-salt" electrolyte enables high-voltage aqueous lithium-ion chemistries[J]. Science, 2015, 350(6263): 938-943. |
| 22 | KONDO Y, MIYAHARA Y, FUKUTSUKA T, et al. Electrochemical intercalation of bis(fluorosulfonyl)amide anions into graphite from aqueous solutions[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2019, 100: 26-29. |
| 23 | ZHU Y P, YIN J, EMWAS A H, et al. An aqueous Mg2+-based dual-ion battery with high power density[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(50): 2107523. |
| 24 | ALI ZAFAR Z, ABBAS G, SILHAVIK M, et al. Reversible anion intercalation into graphite from aluminum perchlorate "water‐in‐salt" electrolyte[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2022, 404: 139754. |
| 25 | ALI ZAFAR Z, ABBAS G, KNIZEK K, et al. Chaotropic anion based "water-in-salt" electrolyte realizes a high voltage Zn-graphite dual-ion battery[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(4): 2064-2074. |
| 26 | CLARISZA A, BEZABH H K, JIANG S K, et al. Highly concentrated salt electrolyte for a highly stable aqueous dual-ion zinc battery[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(32): 36644-36655. |
| 27 | LI H, KURIHARA T, YANG D Y, et al. A novel aqueous dual-ion battery using concentrated bisalt electrolyte[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 38: 454-461. |
| 28 | RODRÍGUEZ-PÉREZ I A, ZHANG L, WROGEMANN J M, et al. Enabling natural graphite in high-voltage aqueous graphite || Zn metal dual-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(41): 2001256. |
| 29 | HUANG Z D, HOU Y, WANG T R, et al. Manipulating anion intercalation enables a high-voltage aqueous dual ion battery[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 3106. |
| 30 | PUTTASWAMY R, MONDAL C, MONDAL D, et al. An account on the deep eutectic solvents-based electrolytes for rechargeable batteries and supercapacitors[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2022, 33: e00477. |
| 31 | SMITH E L, ABBOTT A P, RYDER K S. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and their applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(21): 11060-11082. |
| 32 | WU J X, LIANG Q H, YU X L, et al. Deep eutectic solvents for boosting electrochemical energy storage and conversion: A review and perspective[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(22): 2011102. |
| 33 | KIM K I, GUO Q B, TANG L T, et al. Reversible insertion of Mg-Cl superhalides in graphite as a cathode for aqueous dual-ion batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2020, 59(45): 19924-19928. |
| 34 | SCHMUELLING G, PLACKE T, KLOEPSCH R, et al. X-ray diffraction studies of the electrochemical intercalation of bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide anions into graphite for dual-ion cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 239: 563-571. |
| 35 | MEISTER P, SIOZIOS V, REITER J, et al. Dual-ion cells based on the electrochemical intercalation of asymmetric fluorosulfonyl-(trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide anions into graphite[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 130: 625-633. |
| 36 | KIM K I, TANG L T, MIRABEDINI P, et al. [LiCl2]– superhalide: A new charge carrier for graphite cathode of dual-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(23): 2112709. |
| 37 | WROGEMANN J M, KÜNNE S, HECKMANN A, et al. Development of safe and sustainable dual-ion batteries through hybrid aqueous/nonaqueous electrolytes[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(8): 1902709. |
| 39 | KIM K I, TANG L T, MURATLI J M, et al. A Graphite∥PTCDI aqueous dual-ion battery[J]. ChemSusChem, 2022, 15(5): e202102394. |
| 40 | WANG Z F, LI H F, TANG Z J, et al. Hydrogel electrolytes for flexible aqueous energy storage devices[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(48): 1804560. |
| 41 | CAI S Y, CHU X Y, LIU C, et al. Water-salt oligomers enable supersoluble electrolytes for high-performance aqueous batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(13): e2007470. |
| 42 | LI L W, ZHANG L S, GUO W B, et al. High-performance dual-ion Zn batteries enabled by a polyzwitterionic hydrogel electrolyte with regulated anion/cation transport and suppressed Zn dendrite growth[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(43): 24325-24335. |
| 43 | ZHU J J, XU Y T, FU Y J, et al. Hybrid aqueous/nonaqueous water-in-bisalt electrolyte enables safe dual ion batteries[J]. Small, 2020, 16(17): e1905838. |
| 44 | RÜDORFF W, HOFMANN U. Über graphitsalze[J]. Zeitschrift Für Anorganische Und Allgemeine Chemie, 1938, 238(1): 1-50. |
| 45 | WESSBECHER SKAF D, EDWARDS J K. Electrochemical graphite intercalation with nitric acid solutions[J]. Synthetic Metals, 1992, 46(2): 137-145. |
| 46 | NOEL M, SANTHANAM R, FRANCISCA FLORA M. Comparison of fluoride intercalation/de-intercalation processes on graphite electrodes in aqueous and aqueous methanolic HF media[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 1995, 56(2): 125-131. |
| 47 | SHPIGEL N, MALCHIK F, LEVI M D, et al. New aqueous energy storage devices comprising graphite cathodes, MXene anodes and concentrated sulfuric acid solutions[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 32: 1-10. |
| 48 | SEEL J A, DAHN J R. Electrochemical intercalation of PF6 into graphite[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2000, 147(3): 892. |
| 49 | ZHOU X L, LIU Q R, JIANG C L, et al. Strategies towards low-cost dual-ion batteries with high performance[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2020, 59(10): 3802-3832. |
| 50 | YANG H, SHI X Y, DENG T, et al. Carbon-based dual-ion battery with enhanced capacity and cycling stability[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2018, 5(23): 3612-3618. |
| 51 | GUO Q B, KIM K I, JIANG H, et al. A high-potential anion-insertion carbon cathode for aqueous zinc dual-ion battery[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(38): 2002825. |
| 52 | LU Y, CHEN J. Prospects of organic electrode materials for practical lithium batteries[J]. Nature Reviews Chemistry, 2020, 4: 127-142. |
| 53 | XU Y, ZHOU M, LEI Y. Organic materials for rechargeable sodium-ion batteries[J]. Materials Today, 2018, 21(1): 60-78. |
| 54 | SONG Z P, ZHOU H S. Towards sustainable and versatile energy storage devices: An overview of organic electrode materials[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2013, 6(8): 2280-2301. |
| 55 | WAN F, ZHANG L L, WANG X Y, et al. An aqueous rechargeable zinc-organic battery with hybrid mechanism[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(45): 1804975. |
| 56 | KIM C, AHN B Y, WEI T S, et al. High-power aqueous zinc-ion batteries for customized electronic devices[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(12): 11838-11846. |
| 57 | ZHOU G Y, AN X Y, ZHOU C Y, et al. Highly porous electroactive polyimide-based nanofibrous composite anode for all-organic aqueous ammonium dual-ion batteries[J]. Composites Communications, 2020, 22: 100519. |
| 58 | GE J M, YI X H, FAN L, et al. An all-organic aqueous potassium dual-ion battery[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 57: 28-33. |
| 59 | ZHANG H Z, ZHONG L F, XIE J H, et al. A COF-like N-rich conjugated microporous polytriphenylamine cathode with pseudocapacitive anion storage behavior for high-energy aqueous zinc dual-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(34): e2101857. |
| 60 | CAI Z J, HOU C W. Study on the electrochemical properties of zinc/polyindole secondary battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(24): 10731-10736. |
| 61 | CHEN C X, GAN Z Y, XU C, et al. Electrosynthesis of poly(aniline-co-azure B) for aqueous rechargeable zinc-conducting polymer batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 252: 226-234. |
| 62 | MU S L, SHI Q F. Controllable preparation of poly(aniline-co-5-aminosalicylic acid) nanowires for rechargeable batteries[J]. Synthetic Metals, 2016, 221: 8-14. |
| 63 | CHEN C X, HONG X Z, CHEN A K, et al. Electrochemical properties of poly(aniline-co-N-methylthionine) for zinc-conducting polymer rechargeable batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 190: 240-247. |
| 64 | GLATZ H, LIZUNDIA E, PACIFICO F, et al. An organic cathode based dual-ion aqueous zinc battery enabled by a cellulose membrane[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2019, 2(2): 1288-1294. |
| 65 | KOSHIKA K, SANO N, OYAIZU K, et al. An aqueous, electrolyte-type, rechargeable device utilizing a hydrophilic radical polymer-cathode[J]. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics, 2009, 210(22): 1989-1995. |
| 66 | LUO Y W, ZHENG F P, LIU L J, et al. A high-power aqueous zinc-organic radical battery with tunable operating voltage triggered by selected anions[J]. ChemSusChem, 2020, 13(9): 2239-2244. |
| 67 | XIE J, YU F, ZHAO J W, et al. An irreversible electrolyte anion-doping strategy toward a superior aqueous Zn-organic battery[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 33: 283-289. |
| 68 | LIN Z Q, FAN G H, ZHANG T, et al. Solid-electrolyte interphase for ultra-stable aqueous dual-ion storage[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(7): 2203532. |
| 69 | WANG N, GUO Z W, NI Z G, et al. Molecular tailoring of an n/p-type phenothiazine organic scaffold for zinc batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2021, 60(38): 20826-20832. |
| 70 | ZHANG H, XU D X, WANG L P, et al. A polymer/graphene composite cathode with active carbonyls and secondary amine moieties for high-performance aqueous Zn-organic batteries involving dual-ion mechanism[J]. Small, 2021, 17(25): e2100902. |
| 71 | RODRÍGUEZ-PÉREZ I A, ZHANG L, LEONARD D P, et al. Aqueous anion insertion into a hydrocarbon cathode via a water-in-salt electrolyte[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2019, 109: 106599. |
| 72 | ZHANG C, MA W Y, HAN C Z, et al. Tailoring the linking patterns of polypyrene cathodes for high-performance aqueous Zn dual-ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(1): 462-472. |
| 73 | ZHANG F, ZHANG G W, YAO H, et al. Scalable in situ growth of self-assembled coordination supramolecular network arrays: A novel high-performance energy storage material[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 338: 230-239. |
| 74 | AUBREY M L, LONG J R. A dual-ion battery cathode via oxidative insertion of anions in a metal-organic framework[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(42): 13594-13602. |
| 75 | WANG Z H, YAO H, ZHANG F, et al. Electro-synthesized Ni coordination supermolecular-networks-coated exfoliated graphene composite materials for high-performance asymmetric supercapacitors[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(42): 16476-16483. |
| 76 | TAN Y M, TAO Z R, ZHU Y F, et al. Anchoring I3 - via charge-transfer interaction by a coordination supramolecular network cathode for a high-performance aqueous dual-ion battery[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(42): 47716-47724. |
| 77 | TAN Y M, CHEN Z, TAO Z R, et al. A two-dimensional porphyrin coordination supramolecular network cathode for high-performance aqueous dual-ion battery[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2023, 62(12): e202217744. |
| 78 | JIANG H, WEI Z X, MA L, et al. An aqueous dual-ion battery cathode of Mn3O4 via reversible insertion of nitrate[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(16): 5286-5291. |
| 79 | JIANG H, JI X L. Counter-ion insertion of chloride in Mn3O4 as cathode for dual-ion batteries: A new mechanism of electrosynthesis for reversible anion storage[J]. Carbon Energy, 2020, 2(3): 437-442. |
| 80 | XU X Q, YANG H Q, WANG X L, et al. Efficient high-rate aqueous alkaline battery with dual-ion intercalation chemistry enabled by asymmetric electrode polarization[J]. Cell Reports Physical Science, 2022, 3(8): 100981. |
| 81 | CAO X X, PAN A Q, YIN B, et al. Nanoflake-constructed porous Na3V2(PO4)3/C hierarchical microspheres as a bicontinuous cathode for sodium-ion batteries applications[J]. Nano Energy, 2019, 60: 312-323. |
| 82 | SONG W X, JI X B, WU Z P, et al. First exploration of Na-ion migration pathways in the NASICON structure Na3V2(PO4)3[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(15): 5358-5362. |
| 83 | NI Q, GUO Q B, REN H X, et al. Realizing the multi-electron reaction in the Na3V2(PO4)3 cathode via reversible insertion of dihydrogen phosphate anions[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(1): 1233-1240. |
| 84 | NIAN Q S, LIU S, LIU J, et al. All-climate aqueous dual-ion hybrid battery with ultrahigh rate and ultralong life performance[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2019, 2(6): 4370-4378. |
| 85 | SONG F, HU X L. Exfoliation of layered double hydroxides for enhanced oxygen evolution catalysis[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 4477. |
| 86 | LEE P K, TAN T, WANG S, et al. Robust micron-sized silicon secondary particles anchored by polyimide as high-capacity, high-stability Li-ion battery anode[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(40): 34132-34139. |
| 87 | TIAN B B, ZHENG J, ZHAO C X, et al. Carbonyl-based polyimide and polyquinoneimide for potassium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(16): 9997-10003. |
| 88 | JIANG B, KONG T Y, CAI Z H, et al. In-situ modification of polyimide anode materials in dual-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2022, 435: 141402. |
| 89 | ZHANG Y D, AN Y F, YIN B, et al. A novel aqueous ammonium dual-ion battery based on organic polymers[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(18): 11314-11320. |
| 90 | PERTICARARI S, SAYED-AHMAD-BARAZA Y, EWELS C, et al. Dual anion-cation reversible insertion in a bipyridinium-diamide triad as the negative electrode for aqueous batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(8): 1701988. |
| 91 | TAO Y P, DING C X, TAN D M, et al. Aqueous dual-ion battery based on a hematite anode with exposed{1 0 4}facets[J]. ChemSusChem, 2018, 11(24): 4269-4274. |
| 92 | WU C, KOPOLD P, DING Y L, et al. Synthesizing porous NaTi2(PO4)3 nanoparticles embedded in 3D graphene networks for high-rate and long cycle-life sodium electrodes[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(6): 6610-6618. |
| 93 | CHEN S Q, WU C, SHEN L F, et al. Challenges and perspectives for NASICON-type electrode materials for advanced sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(48): 1700431. |
| 94 | ZHANG Z S, HU X Q, ZHOU Y, et al. Aqueous rechargeable dual-ion battery based on fluoride ion and sodium ion electrochemistry[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(18): 8244-8250. |
| 95 | YU H X, DENG C C, YAN H H, et al. Cu3(PO4)2: Novel anion convertor for aqueous dual-ion battery[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2021, 13(1): 41. |
| [1] | 彭可, 张志成, 胡有章, 张旭辉, 周稼辉, 李彬. 基于有限元的热力耦合场匣钵运动分析与优化[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(2): 634-642. |
| [2] | 杜文, 王君雷, 徐运飞, 李世龙, 王昆. 火焰喷雾热解法生产锂离子电池高镍三元正极材料的技术经济分析[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(1): 345-357. |
| [3] | 陈珊珊, 郑翔, 王若, 原铭蔓, 彭威, 鲁博明, 张光照, 王朝阳, 王军, 邓永红. 锂离子电池硅基负极电解液添加剂研究进展:挑战与展望[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(1): 279-292. |
| [4] | 戴雪娇, 闫婕, 王管, 董浩天, 蒋丹枫, 魏泽威, 孟凡星, 刘松涛, 张海涛. 铌基低温电池关键材料研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(1): 311-324. |
| [5] | 李顺, 黄建国, 何桂金. 木质素基碳/硫纳米球复合材料作为高性能锂硫电池正极材料[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(1): 270-278. |
| [6] | 王盼晴, 黄彦杰, 何一芃, 陈祁恒, 尹提, 陈伟豪, 谭磊, 宁天翔, 邹康宇, 李灵均. 高镍正极材料表面锂残渣的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(1): 92-112. |
| [7] | 陈淑媛, 程晨, 夏啸, 鞠焕鑫, 张亮. 高比能二次电池正极材料的X射线谱学研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(1): 113-129. |
| [8] | 张新新, 申晓宇, 岑官骏, 乔荣涵, 朱璟, 郝峻丰, 孙蔷馥, 田孟羽, 金周, 詹元杰, 武怿达, 闫勇, 贲留斌, 俞海龙, 刘燕燕, 黄学杰. 锂电池百篇论文点评(2023.10.1—2023.11.30)[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(1): 252-269. |
| [9] | 贾铭勋, 吴桐, 杨道通, 秦小茜, 刘景海, 段莉梅. 锂硫电池电解液多功能添加剂:作用机制及先进表征[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(1): 36-47. |
| [10] | 张永辉, 傅杰, 李先锋, 张长昆. 原位表征技术在水系有机液流电池中的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(9): 2971-2984. |
| [11] | 詹世英, 李欢欢, 胡方. 水系锌离子电容器正极材料的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(9): 2799-2810. |
| [12] | 周向阳, 胡颖杰, 梁家浩, 周其杰, 文康, 陈松, 杨娟, 唐晶晶. 天然鳞片石墨球化尾料的高性能负极材料制备及储锂特性研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(9): 2767-2777. |
| [13] | 江婉薇, 梁呈景, 钱历, 刘梅城, 朱孟想, 马骏. 锡基三维石墨烯泡沫调控及其锂电池负极性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(9): 2746-2751. |
| [14] | 岑官骏, 乔荣涵, 申晓宇, 朱璟, 郝峻丰, 孙蔷馥, 张新新, 田孟羽, 金周, 詹元杰, 武怿达, 闫勇, 贲留斌, 俞海龙, 刘燕燕, 黄学杰. 锂电池百篇论文点评(2023.6.1—2023.7.31)[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(9): 3003-3018. |
| [15] | 张鼎, 叶子贤, 刘镇铭, 易群, 史利娟, 郭慧娟, 黄毅, 王莉, 何向明. 钠离子电池黑磷基负极材料研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(8): 2482-2490. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
