Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2023, Vol. 12 ›› Issue (8): 2491-2503.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0180
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yu HAN1( ), Shengling CAO1, Jing NING1, Kangli WANG2, Kai JIANG2, Min ZHOU2(
), Shengling CAO1, Jing NING1, Kangli WANG2, Kai JIANG2, Min ZHOU2( )
)
Received:2023-03-30
Revised:2023-04-09
Online:2023-08-05
Published:2023-08-23
Contact:
Min ZHOU
E-mail:hanyu1588@qq.com;minzhou0729@hust.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Yu HAN, Shengling CAO, Jing NING, Kangli WANG, Kai JIANG, Min ZHOU. Strategies for interfacial modification in lithium metal batteries with polymers[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(8): 2491-2503.
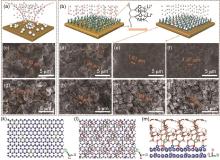
Fig. 6
Li nucleation on the bare Cu foil and PNIPAM grafted Cu substrates (a), (b) Illustration of Li nucleation on the bare Cu foil and PNIPAM grafted Cu substrates; (c), (g) SEM images of Li nucleation on bare Cu foil; (d), (h) SEM images of Li nucleation on the PNIPAM-1@Cu substrate; (e), (i) SEM images of Li nucleation on PNIPAM-2@Cu substrate; (f), (j) SEM images of Li nucleation on PNIPAM-3@Cu substrate; (c)—(f) at the current densities of 0.1 mA/cm2; (g)—(j) at the current densities of 0.5 mA/cm2; (k), (l) Top-view simulation images of the distribution of electrodeposition Li atoms on bare Cu foil and PNIPAM polymer brushes grafted Cu substrate, respectively; (m) Cross-sectional simulation image of the electrodeposition Li atoms on PNIPAM polymer-brush-grafted Cu substrate"
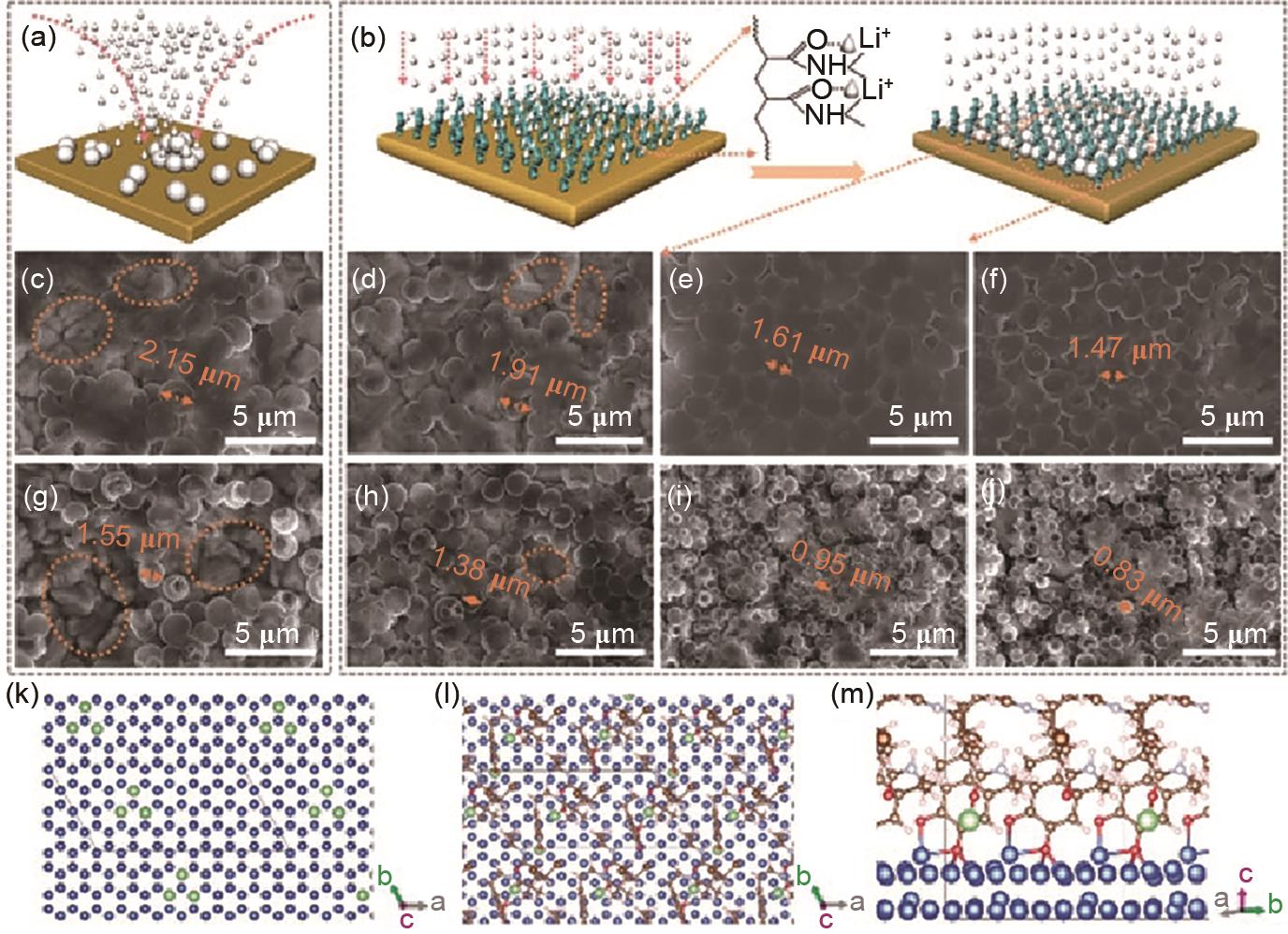

Fig. 7
SEM images of the morphology of Li deposited on pristine Cu and PDA-Cu current collectors after different cycles; (a), (e), (i) Cross view and (b), (f), (j) Top view SEM images of the pristine Cu current collector; (c), (g), (k) Cross view and (d), (h), (l) Top view SEM images of the PDA-Cu current collector"
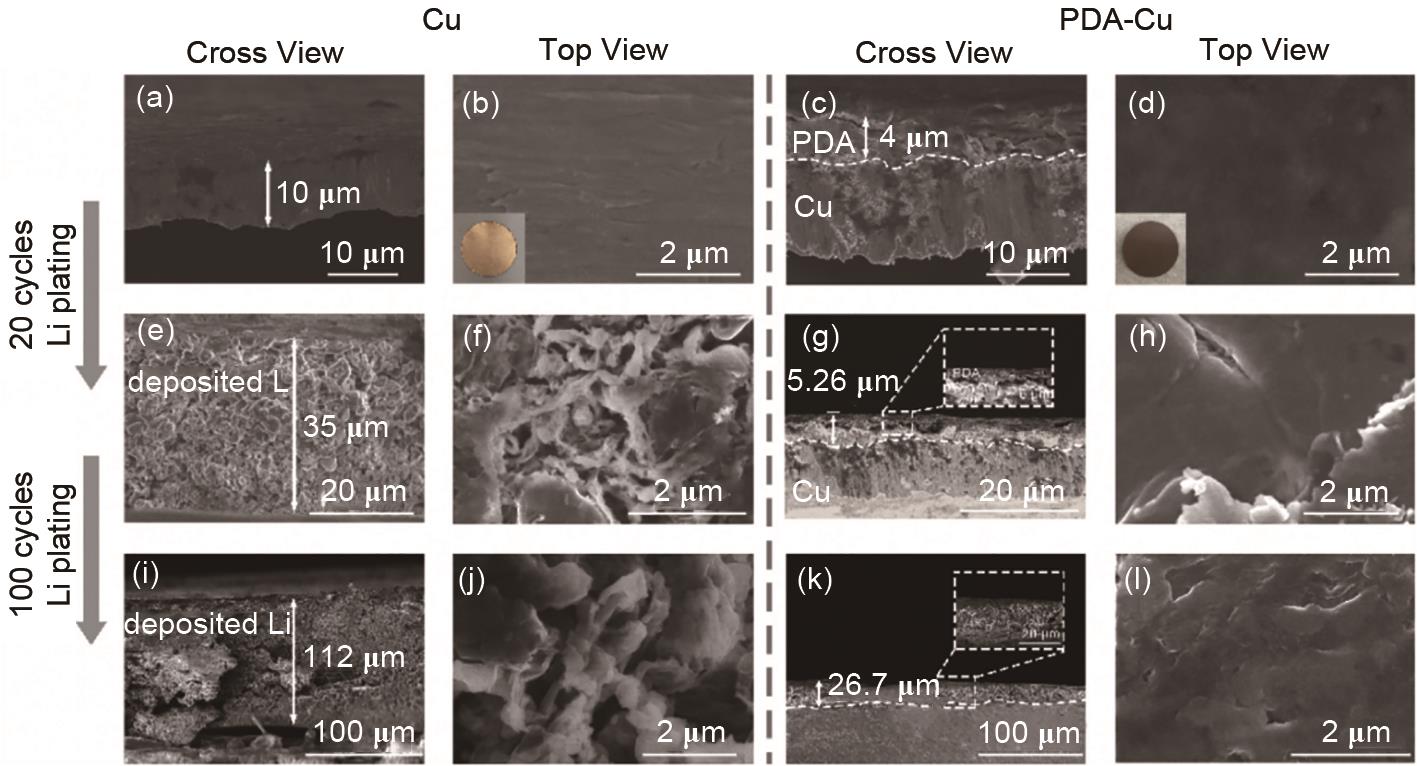

Fig. 10
Schematic illustrations of structure and Li plating behaviour for artificial SEI layers (a) conventional organic-inorganic composite layers based on solid inorganic nanofillers; (b) all-organic composite layers based on rigid and porous xPCMS-g-PEGMA nanofillers prepared by grafting flexible Li+ conductive PEGMA brushes from xPCMS nanospheres, followed by compositing with single-ion-conductive LN"

| 1 | ARMAND M, TARASCON J M. Building better batteries[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7179): 652-657. |
| 2 | LIN D C, LIU Y Y, CUI Y. Reviving the lithium metal anode for high-energy batteries[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2017, 12(3): 194-206. |
| 3 | SCHMUCH R, WAGNER R, HÖRPEL G, et al. Performance and cost of materials for lithium-based rechargeable automotive batteries[J]. Nature Energy, 2018, 3(4): 267-278. |
| 4 | 姚诗言, 曾立艳, 刘军. 高性能锂金属电池负极结构设计及界面强化研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(16): 192-202. |
| YAO S Y, ZENG L Y, LIU J. Research progress in structure design and interface enhancement of lithium anode for high-performance lithium metal batteries[J]. Materials Reports, 2022, 36(16): 192-202. | |
| 5 | BRUCE P G, FREUNBERGER S A, HARDWICK L J, et al. Li-O2 and Li-S batteries with high energy storage[J]. Nature Materials, 2012, 11(1): 19-29. |
| 6 | GAO M D, LI H, XU L, et al. Lithium metal batteries for high energy density: Fundamental electrochemistry and challenges[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 59: 666-687. |
| 7 | XU K. Electrolytes and interphases in Li-ion batteries and beyond[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(23): 11503-11618. |
| 8 | QIN K Q, HOLGUIN K, MOHAMMADIROUDBARI M, et al. Strategies in structure and electrolyte design for high-performance lithium metal batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(15): doi: 10.1002/adfm.202009694. |
| 9 | PELED E, MENKIN S. Review—SEI: Past, present and future[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2017, 164(7): doi: 10.1149/2.1441707jes. |
| 10 | SHI Y, LIU G X, WAN J, et al. In-situ nanoscale insights into the evolution of solid electrolyte interphase shells: Revealing interfacial degradation in lithium metal batteries[J]. Science China Chemistry, 2021, 64(5): 734-738. |
| 11 | LOPEZ J, PEI A, OH J Y, et al. Effects of polymer coatings on electrodeposited lithium metal[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(37): 11735-11744. |
| 12 | SHEN X, ZHANG R, CHEN X A, et al. The failure of solid electrolyte interphase on Li metal anode: Structural uniformity or mechanical strength?[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(10): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201903645. |
| 13 | HE Y, XU H W, SHI J L, et al. Polydopamine coating layer modified current collector for dendrite-free Li metal anode[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 23: 418-426. |
| 14 | LIU W, LIU P C, MITLIN D. Review of emerging concepts in SEI analysis and artificial SEI membranes for lithium, sodium, and potassium metal battery anodes[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(43): doi: 10.1002/aenm.202002297. |
| 15 | LIANG Z, ZHENG G Y, LIU C, et al. Polymer nanofiber-guided uniform lithium deposition for battery electrodes[J]. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(5): 2910-2916. |
| 16 | STARK J K, DING Y, KOHL P A. Nucleation of electrodeposited lithium metal: Dendritic growth and the effect of co-deposited sodium[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2013, 160(9): doi: 10.1149/2.028309jes. |
| 17 | COHEN Y S, COHEN Y, AURBACH D. Micromorphological studies of lithium electrodes in alkyl carbonate solutions using in situ atomic force microscopy[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2000, 104(51): 12282-12291. |
| 18 | CHAZALVIEL J. Electrochemical aspects of the generation of ramified metallic electrodeposits[J]. Physical Review A, Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics, 1990, 42(12): 7355-7367. |
| 19 | ROSSO M, BRISSOT C, TEYSSOT A, et al. Dendrite short-circuit and fuse effect on Li/polymer/Li cells[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2006, 51(25): 5334-5340. |
| 20 | DING F, XU W, GRAFF G L, et al. Dendrite-free lithium deposition via self-healing electrostatic shield mechanism[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(11): 4450-4456. |
| 21 | TU Z Y, NATH P, LU Y Y, et al. Nanostructured electrolytes for stable lithium electrodeposition in secondary batteries[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2015, 48(11): 2947-2956. |
| 22 | JIE Y L, REN X D, CAO R G, et al. Advanced liquid electrolytes for rechargeable Li metal batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(25): doi: 10.1002/adfm.201910777. |
| 23 | 冯建文, 胡时光, 韩兵, 等. 锂金属电池电解液组分调控的研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2020, 9(6): 1629-1640. |
| FENG J W, HU S G, HAN B, et al. Research progress of electrolyte optimization for lithium metal batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2020, 9(6): 1629-1640. | |
| 24 | JEONG H, JANG J, JO C. A review on current collector coating methods for next-generation batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 446: doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.136860. |
| 25 | ZHOU B X, BONAKDARPOUR A, STOŠEVSKI I, et al. Modification of Cu current collectors for lithium metal batteries-A review[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2022, 130: doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2022.100996. |
| 26 | SU L S, MANTHIRAM A. Lithium-metal batteries via suppressing Li dendrite growth and improving coulombic efficiency[J]. Small Structures, 2022, 3(10): doi: 10.1002/sstr.202200114. |
| 27 | SHAO A H, TANG X Y, ZHANG M, et al. Challenges, strategies, and prospects of the anode-free lithium metal batteries[J]. Advanced Energy and Sustainability Research, 2022, 3(4): doi: 10.1002/aesr.202100197. |
| 28 | QI M P, XIE L L, HAN Q, et al. An overview of the key challenges and strategies for lithium metal anodes[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2022, 47: doi: 10.1016/j.est.2021.103641. |
| 29 | ALBERTUS P, BABINEC S, LITZELMAN S, et al. Status and challenges in enabling the lithium metal electrode for high-energy and low-cost rechargeable batteries[J]. Nature Energy, 2018, 3(1): 16-21. |
| 30 | MA L B, CUI J, YAO S S, et al. Dendrite-free lithium metal and sodium metal batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 27: 522-554. |
| 31 | ZHU P C, GASTOL D, MARSHALL J, et al. A review of current collectors for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 485: doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.229321. |
| 32 | XU H Y, LI Q A, PAN H Y, et al. Artificial solid electrolyte interphase based on polyacrylonitrile for homogenous and dendrite-free deposition of lithium metal[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2019, 28(7): doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/28/7/078202. |
| 33 | LANG J L, SONG J N, QI L H, et al. Uniform lithium deposition induced by polyacrylonitrile submicron fiber array for stable lithium metal anode[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(12): 10360-10365. |
| 34 | LI N, YE Q A, ZHANG K, et al. Normalized lithium growth from the nucleation stage for dendrite-free lithium metal anodes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(50): 18246-18251. |
| 35 | LIU T C, GE J X, XU Y, et al. Organic supramolecular protective layer with rearranged and defensive Li deposition for stable and dendrite-free lithium metal anode[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 32: 261-271. |
| 36 | HAO Z D, ZHAO Q, TANG J D, et al. Functional separators towards the suppression of lithium dendrites for rechargeable high-energy batteries[J]. Materials Horizons, 2021, 8(1): 12-32. |
| 37 | ZHANG Z Y, LAI Y Q, ZHANG Z A, et al. Al2O3-coated porous separator for enhanced electrochemical performance of lithium sulfur batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 129: 55-61. |
| 38 | PAN R J, SUN R, WANG Z H, et al. Double-sided conductive separators for lithium-metal batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 21: 464-473. |
| 39 | HAN D H, ZHANG M, LU P X, et al. A multifunctional separator with Mg(OH)2 nanoflake coatings for safe lithium-metal batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 52: 75-83. |
| 40 | LIU K, BAI P, BAZANT M Z, et al. A soft non-porous separator and its effectiveness in stabilizing Li metal anodes cycling at 10 mA/cm2 observed in situ in a capillary cell[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(9): 4300-4307. |
| 41 | WANG W, LIAO C, LIEW K M, et al. A 3D flexible and robust HAPs/PVA separator prepared by a freezing-drying method for safe lithium metal batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(12): 6859-6868. |
| 42 | RYOU M H, LEE D J, LEE J N, et al. Excellent cycle life of lithium-metal anodes in lithium-ion batteries with mussel-inspired polydopamine-coated separators[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2012, 2(6): 645-650. |
| 43 | YAO W, XU M, QIU W J, et al. Ultralight PEDOT functionalized separators toward high-performance lithium metal anodes[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2021, 8(15): 2836-2845. |
| 44 | WANG Z H, PAN R J, XU C, et al. Conducting polymer paper-derived separators for lithium metal batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2018, 13: 283-292. |
| 45 | FU X L, SHANG C Q, YANG M Y, et al. An ion-conductive separator for high safety Li metal batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 475: doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228687. |
| 46 | LI N W, SHI Y, YIN Y X, et al. A flexible solid electrolyte interphase layer for long-life lithium metal anodes[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2018, 57(6): 1505-1509. |
| 47 | LI S M, HUANG J L, CUI Y, et al. A robust all-organic protective layer towards ultrahigh-rate and large-capacity Li metal anodes[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2022, 17(6): 613-621. |
| 48 | DONG Q Y, HONG B, FAN H L, et al. A self-adapting artificial SEI layer enables superdense lithium deposition for high performance lithium anode[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 45: 1220-1228. |
| 49 | GUAN M R, HUANG Y X, MENG Q Q, et al. Stabilization of lithium metal interfaces by constructing composite artificial solid electrolyte interface with mesoporous TiO2 and perfluoropolymers[J]. Small, 2022, 18(40): doi: 10.1002/smll.202202981. |
| [1] | Huan LIU, Na PENG, Qingwen GAO, Wenpeng LI, Zhirong YANG, Jingtao WANG. Crown ether-doped polymer solid electrolyte for high-performance all-solid-state lithium batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(8): 2401-2411. |
| [2] | Lingxuan LI, Zixuan WANG, Chenzi ZHAO, Rui ZHANG, Yang LU, Jiaqi HUANG, Aibing CHEN, Qiang ZHANG. A review of numerical models for composite lithium metal anodes [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(7): 2059-2078. |
| [3] | Lingfeng HUANG, Dongmei HAN, Sheng HUANG, Shuanjin WANG, Min XIAO, Yuezhong MENG. Research progress of polymer electrolytes containing organoboron for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(6): 1815-1830. |
| [4] | Xin SHEN, Rui ZHANG, Chenzi ZHAO, Peng WU, Yutong ZHANG, Jundong ZHANG, Lizhen FAN, Quanbing LIU, Aibing CHEN, Qiang ZHANG. Recent advances in mechano-electrochemistry in lithium metal batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 2781-2797. |
| [5] | Jianxiang DENG, Jinliang ZHAO, Chengde HUANG. High energy density lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(7): 2092-2102. |
| [6] | OU Yu, HOU Wenhui, LIU Kai. Research progress of smart safety electrolytes in lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1772-1787. |
| [7] | ZHOU Weidong, HUANG Qiu, XIE Xiaoxin, CHEN Kejun, LI Wei, QIU Jieshan. Research progress of polymer electrolyte for solid state lithium batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1788-1805. |
| [8] | WANG Can, MA Pan, ZHU Guoliang, WEI Shuimiao, YANG Zhilu, ZHANG Zhiyu. Effect of lithium acrylic-coated nature graphite on its electrochemical properties [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1706-1714. |
| [9] | Xingxing WANG, Ziyu SONG, Hao WU, Wenfang FENG, Zhibin ZHOU, Heng ZHANG. Advances in conducting lithium salts for solid polymer electrolytes [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(4): 1226-1235. |
| [10] | Liang FANG, Kai ZHANG, Limin ZHOU. Recent advances and prospects of electrolyte for aluminum ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(4): 1236-1245. |
| [11] | Dongge QIAO, Xunliang LIU, Zhi WEN, Ruifeng DOU, Wenning ZHOU. Numerical analysis of inhibition of lithium dendrite growth by heating and pulse charging [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(3): 1008-1018. |
| [12] | Suting WENG, Zepeng LIU, Gaojing YANG, Simeng ZHANG, Xiao ZHANG, Qiu FANG, Yejing LI, Zhaoxiang WANG, Xuefeng WANG, Liquan CHEN. Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) characterizing beam-sensitive materials in lithium metal batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(3): 760-780. |
| [13] | Luyu GAN, Rusong CHEN, Hongyi PAN, Siyuan WU, Xiqian YU, Hong LI. Multiscale research strategy of lithium ion battery safety issue: Experimental and simulation methods [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(3): 852-865. |
| [14] | Yubo QI, Da GAO, Xianling ZHENG. Economic analysis of SPE hydrogen production technology in China [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(12): 4038-4047. |
| [15] | Xiubo ZHANG, Chang YU, Jinhe YU, Yingbin LIU, Yuanyang XIE, Jianjian WANG, Shuqin LAN, Jieshan QIU. Recent progress of polymer electrolytes for supercapacitors under extreme environments [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(12): 3808-3818. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
