Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2025, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (6): 2215-2222.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.1164
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Dandan HAN1( ), Wuwei ZHANG2, Liang ZHANG1, Zongjiang WANG1(
), Wuwei ZHANG2, Liang ZHANG1, Zongjiang WANG1( )
)
Received:2024-12-12
Revised:2025-03-03
Online:2025-06-28
Published:2025-06-27
Contact:
Zongjiang WANG
E-mail:376518692@qq.com;18164976034@163.com
CLC Number:
Dandan HAN, Wuwei ZHANG, Liang ZHANG, Zongjiang WANG. Design and electrochemical performance of LiMn1-y Fe y PO4/C cathode materials with a core-shell structure[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(6): 2215-2222.
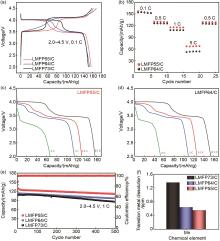
Fig. 3
(a) First charge/discharge curves of LMFP55/C, LMFP64/C and LMFP73/C at 0.1 C; (b) Rate performance of LMFP55/C and LMFP64/C; (c), (d) Discharge curves of LMFP55/C and LMFP64/C at different rate; (e) Cycling performance of LMFP55/C, LMFP64/C and LMFP73/C at 1 C; (f) Transition metal dissolution content of LMFP55/C, LMFP64/C and LMFP73/C after 500 cycles at 1 C"
| 1 | LUO B, XIAO S, LI Y Y, et al. The improved electrochemical performances of LiMn1- xFexPO4 solid solutions as cathodes for Lithium-ion batteries[J]. Materials Technology, 2017, 32(4): 272-278. DOI: 10.1080/10667857.2016.1214664. |
| 2 | QI M Y, WANG L, HUANG X L, et al. Surface engineering of cathode materials: Enhancing the high performance of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Small, 2024, 20(38): 2402443. DOI: 10.1002/smll. 202402443. |
| 3 | ZHANG C, SUNARSO J, LIU S M. Designing CO2-resistant oxygen-selective mixed ionic-electronic conducting membranes: Guidelines, recent advances, and forward directions[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(10): 2941-3005. DOI: 10.1039/C6CS00841K. |
| 4 | 李晨威, 徐世国, 余海峰, 等. 镁掺杂改性LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4/C正极材料与性能研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(6): 1767-1774. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0942. |
| LI C W, XU S G, YU H F, et al. Synthesis of Mg-doped LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4/C cathode materials for Li-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(6): 1767-1774. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0942. | |
| 5 | 唐振强, 蔡宗英, 曹卫刚, 等. 橄榄石型磷酸铁锂正极材料的合成及改性研究进展[J/OL]. 无机盐工业, 1-14[2024-11-19]. https://doi.org/10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2024-0281. |
| 6 | HUYNH L T N, LE P P N, TRINH V D, et al. Structure and electrochemical behavior of minor Mn-doped olivine LiMnxFe1- xPO4[J]. Journal of Chemistry, 2019, 2019(1): 5638590. DOI: 10.1155/2019/5638590. |
| 7 | JEONG B J, SUNG J Y, JIANG F, et al. Providing high stability to suppress metal dissolution in LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 cathode materials by Zn doping[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 96: 112552. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2024.112552. |
| 8 | HOU H Y, YE M, LAN J, et al. High Li-storage performances of LiMnxFe1- xPO4/C (x = 0, 0.05, 0.1 and 0.2) cathodes derived from spent Li foil, expired manganese gluconate and rust[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 78: 110176. DOI: 10.1016/j.est. 2023. 110176. |
| 9 | ZHANG K, LI Z X, LI X, et al. Perspective on cycling stability of lithium-iron manganese phosphate for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Rare Metals, 2023, 42(3): 740-750. DOI: 10.1007/s12598-022-02107-w. |
| 10 | TRINH D V, NGUYEN M T T, DANG H T M, et al. Hydrothermally synthesized nanostructured LiMnxFe1- xPO4 (x = 0-0.3) cathode materials with enhanced properties for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11: 12280. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-91881-1. |
| 11 | AHMAD WANI T, SURESH G. A comprehensive review of LiMnPO4 based cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries: Current strategies to improve its performance[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 44: 103307. DOI: 10.1016/j.est. 2021. 103307. |
| 12 | ZHANG B, WANG X J, LI H, et al. Electrochemical performances of LiFe1- xMnxPO4 with high Mn content[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(16): 6992-6996. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2010.10.051. |
| 13 | ZHANG B C, XIE X M, PENG Z D, et al. Synthesis of flexible LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C microsphere and its synergetic effects with blended LiNi0.85Co0.10Al0.05O2 electrodes[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 541: 231671. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour. 2022. 231671. |
| 14 | LIU X C, OUYANG B X, HAO R, et al. Li2SiO3 modification of C/LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4 for high performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2022, 9(16): e202200609. DOI: 10.1002/celc.202200609. |
| 15 | HU Q, LIAO J Y, XIAO X, et al. Ultrahigh rate capability of manganese based olivine cathodes enabled by interfacial electron transport enhancement[J]. Nano Energy, 2022, 104: 107895. DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.107895. |
| 16 | RUAN T T, WANG B, WANG F, et al. Stabilizing the structure of LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 via the formation of concentration-gradient hollow spheres with Fe-rich surfaces[J]. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(9): 3933-3944. DOI: 10.1039/c8nr10224d. |
| 17 | PARK K, KIM J, WI S, et al. Optimum morphology of mixed-olivine mesocrystals for a Li-ion battery[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2018, 57(10): 5999-6009. DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b00501. |
| 18 | HU H, LI H, LEI Y, et al. Mg-doped LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C nano-plate as a high-performance cathode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 73: 109006. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2023.109006. |
| 19 | ZHANG K C, CAO J R, TIAN S Y, et al. The prepared and electrochemical property of Mg-doped LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4/C as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Ionics, 2021, 27(11): 4629-4637. DOI: 10.1007/s11581-021-04183-x. |
| 20 | LIU S J, ZHENG J G, ZHANG B, et al. Engineering manganese-rich phospho-olivine cathode materials with exposed crystal{010}facets for practical Li-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 454: 139986. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.139986. |
| 21 | XIE X M, ZHANG B C, HU G R, et al. A new route for green synthesis of LiFe0.25Mn0.75PO4/C@rGO material for lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 853: 157106. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157106. |
| 22 | WANG Y Z, HU G R, CAO Y B, et al. Highly atom-economical and environmentally friendly synthesis of LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/rGO/C cathode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 354: 136743. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136743. |
| 23 | CHEN L, YAN B, WANG H Y, et al. Synthesis and characterization of 0.95LiMn0.95Fe0.05PO4·0.05Li3V2(PO4)3 nanocomposite by sol-gel method[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 287: 316-322. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.04.075. |
| 24 | OH S M, MYUNG S T, PARK J B, et al. Double-structured LiMn0.85Fe0.15PO4 coordinated with LiFePO4 for rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(8): 1853-1856. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201107394. |
| 25 | LIU J L, WU Y Q, ZHANG B, et al. A promising solid-state synthesis of LiMn1- yFeyPO4 cathode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Small, 2024, 20(14): 2309629. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202309629. |
| 26 | WEN F, LV T A, GAO P, et al. Graphene-embedded LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 composites with promoted electrochemical performance for lithium ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018, 276: 134-141. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2018.04.157. |
| 27 | 于松民, 金洪波, 杨明虎, 等. 氟掺杂改性LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4正极材料及其电化学性能[J]. 化工进展, 2024, 43(1): 302-309. DOI: 10. 16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2023-1224. |
| YU S M, JIN H B, YANG M H, et al. Synthesis and modification of F-doped olivine LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 cathode materials for Li-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2024, 43(1): 302-309. DOI: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2023-1224. | |
| 28 | XU X Y, WANG T, BI Y J, et al. Improvement of electrochemical activity of LiMnPO4-based cathode by surface iron enrichment[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 341: 175-182. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.12.001. |
| 29 | YANG L T, XIA Y G, QIN L F, et al. Concentration-gradient LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 cathode material for high performance lithium ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 304: 293-300. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.11.037. |
| 30 | LIU X Z, ZHANG Y, MENG Y S, et al. Influence mechanism of Mg2+ doping on electrochemical properties of LiFePO4 cathode materials[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2022, 5(7): 8452-8459. DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.2c00986. |
| 31 | CHEN Z W, WANG W G, DUAN J G, et al. Highly efficient synthesis of nano LiMn0.90Fe0.10PO4/C composite via mechanochemical activation assisted calcination[J]. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(11): 18483-18490. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2023.02.221. |
| 32 | ZOU B K, WANG H Y, QIANG Z Y, et al. Mixed-carbon-coated LiMn0.4Fe0.6PO4 nanopowders with excellent high rate and low temperature performances for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 196: 377-385. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta. 2016.03.017. |
| 33 | YU M, LI J, NING X H. Improving electrochemical performance of LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 cathode by hybrid coating of Li3VO4 and carbon[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 368: 137597. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2020.137597. |
| 34 | PENG Z D, ZHANG B C, HU G R, et al. Green and efficient synthesis of micro-nano LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C composite with high-rate performance for Li-ion battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 387: 138456. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2021.138456. |
| [1] | Zheng CHEN, Gongdong DUO, Jiangwei SHEN, Shiquan SHEN, Yu LIU, Fuxing WEI. State of health estimation for lithium battery based on incremental capacity analysis and VMD-GWO-KELM [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(6): 2476-2487. |
| [2] | Jingjing RUAN, Xiangkun WU, Yonghui LI, Chongchong ZHAO, Shenshen LI, Tongfei WANG, Shengjie LIANG, Guihong GAO. Preparation and performance studies of low-cost graphite thick dry electrodes [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(6): 2248-2255. |
| [3] | Yingjian CHEN, Shang WU, Yuancheng CAO, Baoshuai DU, Zhenxing WANG, Zhongwen OUYANG, Shun TANG. Application of magnetic separation in the recycling of cathode and anode materials from spent lithium batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(5): 1918-1927. |
| [4] | Qiangfu SUN, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Jing ZHU, Junfeng HAO, Xinxin ZHANG, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Hong ZHOU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Feb. 1, 2025 to March 31, 2025) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(5): 1727-1747. |
| [5] | Xiaolan WU, Pengjie MA, Zhifeng BAI, Chenglong LIU, Guifang GUO, Jinhua ZHANG. A kind of intelligent PID double-layer active balancing control method for lithium-ion battery pack [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(3): 1150-1159. |
| [6] | Nan LI, Jing MA, Tingxiu HUANG, Yixing SHEN, Min SHEN, Yiyi JIANG, Tao HONG, Guoqiang MA, Zifeng MA. Research progress on nitrile compounds in high potential electrolytes [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(3): 997-1009. |
| [7] | Chencheng XU, Zhan WANG, Shuang LI, Jiangmin JIANG, Zhicheng JU. Research progress and engineering application prospects of prelithiation technology for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(3): 930-946. |
| [8] | Liping ZHOU, Deqing ZHOU, Fenghua ZHENG, Qichang PAN, Sijiang HU, Yongjie JIANG, Hongqiang WANG, Qingyu LI. Preparation and application of Si@void@C composite anode materials for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(3): 1115-1122. |
| [9] | Xinxin ZHANG, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Jing ZHU, Junfeng HAO, Qiangfu SUN, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Hong ZHOU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of 100 selected recent papers on lithium batteries (December 1, 2024 to January 31, 2025) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(3): 1310-1330. |
| [10] | Boyu LIU, Tengfei WANG, Qing PANG, Kaiyu CHEN, Hongyu WANG. Preparation and electrochemical performance of Mg-Cr co-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(3): 1097-1106. |
| [11] | Jiabo LI, Zhixuan WANG, Di TIAN, Zhonglin SUN. Prediction method for remaining service life of lithium batteries using SSA-LSTM combination under variable mode decomposition [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(2): 659-670. |
| [12] | Jianru ZHANG, Qiyu WANG, Yinghui JI, Xin GAO, Xiqian YU, Hong LI. Application of Auger electron spectroscopy in the analysis of lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(2): 755-769. |
| [13] | Heyu LI, Xiaobo HONG, Zihan CHEN, Dianbo RUAN. The effect of porous heat insulation plate on the heat spread barrier of lithium-ion battery module [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(2): 479-487. |
| [14] | Lishuai ZHANG, Yifei ZHANG, Yiyang MA, Sibo ZHAO, Hongquan LIU, Shengting SHI, Yanjun ZHONG. Research progress on sodium-ion battery cathode materials based on iron-based prussian blue analogues [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(2): 525-543. |
| [15] | Jianxuan LI, Chen LIN, Zhongkai ZHOU. State of health estimation based on subtraction average based optimizer and bidirectional long and short term memory networks for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(1): 358-369. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
