Energy Storage Science and Technology
Yu JIA( ), Hui CHEN, Mengna LIU, Ximing ZHAO, Long QU(
), Hui CHEN, Mengna LIU, Ximing ZHAO, Long QU( )
)
Received:2025-09-19
Revised:2025-11-14
Contact:
Long QU
E-mail:2023205051@cqust.edu.cn;longqu@cqust.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Yu JIA, Hui CHEN, Mengna LIU, Ximing ZHAO, Long QU. Recent advances in a controllable synthesis of LiMnₓFe1-xPO4 cathodes via co-precipitation methods[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2025.0852.
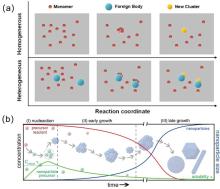
Figure 3
(a) Schematic diagram of homogeneous nucleation and heterogeneous nucleation[41]; (b) Schematic diagram of the Lamer model: time-dependent evolution of reactant (red), reactant concentration (green), and particle size (blue), illustrating three typical stages of crystal formation in solution. Stage I: Supersaturation continuously accumulates but does not reach the critical nucleation concentration, and no nucleation occurs; Stage II: Supersaturation exceeds the critical value, triggering burst homogeneous nucleation, while supersaturation rapidly decreases; Stage III: Supersaturation drops below the critical value, nucleation ceases, and the growth stage begins[45]."
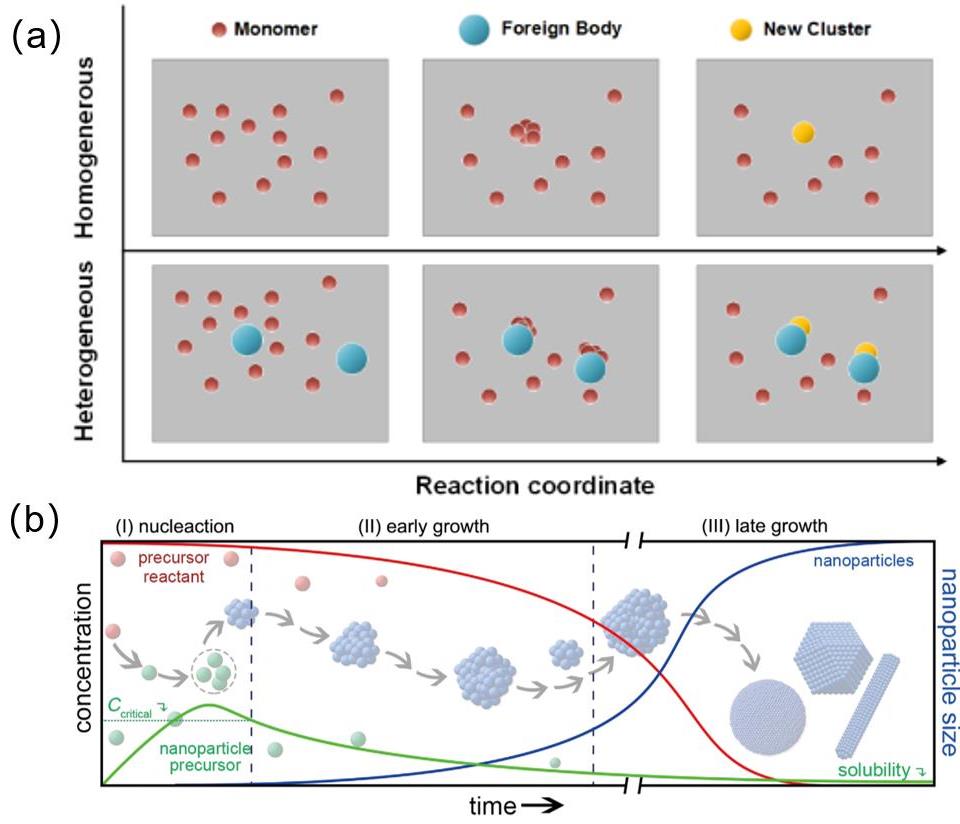
Fig. 4
Thermodynamic equilibrium analysis of the Mn2+-Fe2+-Mg2+-C2O42--H2O system:(a)~(c)Three-dimensional relationship plots of oxalate excess coefficient, pH, and the logarithm of total metal concentration; (d) Optimization results of precipitation conditions; (e) EDS mapping of Li(Fe0.4Mn0.8)0.97Mg0.03PO4/C[31]"

Table1
Comparative summary of LiMnxFe1-xPO4/C synthesized from different precursors Note: The data listed in this table are for fundamental materials without specific modifications, in order to compare the influence of the precursors themselves"
| 前驱体类型 | 合成条件 | 产品特性 | 电化学性能(mAh/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MnxFe1-xPO4 | 沉淀剂:H3PO4 溶剂:有机溶剂(如乙醇) pH:<2 添加剂:HNO3、H2O2等做氧化剂 其他:后续煅烧需H2或还原碳 | 颗粒内部具有纳米尺度的孔隙结构,易于提升体积能量密度 | 140.3(0.1C)、79.6(5C)[ 140.2(0.1C)、100.3(3C)[ 140.4(0.1C)、109.6(5C)[ |
| (MnₓFe1-x)3(PO4)2 | 沉淀剂:NH4H2PO4 溶剂:水 pH:≈6.5(氨水调节) 气氛:N2 | 环境友好,锂化无需还原碳 | 140.1(0.1C)[ 150.6(0.1C)、110.1(5C)[ 151.2(0.1C)、98.8(5C)[ |
| NH4MnxFe1-xPO4 | 沉淀剂:(NH4)2HPO4 溶剂:水 pH:近中性 气氛:N2 | 结构相容性好,转化动力学优势,离子交换高效 | 145.6(0.1C)、125.3(5C)[ 139.1(0.1C)[ 146.9(0.1C)、119.8(5C)[ 140.1(0.1C)、100.6(5C)[ |
| MnₓFe1-xC2O4 | 沉淀剂:草酸、草酸铵、草酸钠 溶剂:水 pH:≈4.5 温度:90℃(控制相分离) 添加剂:抗坏血酸 | 分解温度低于锂化温度,且在分解过程中体积变化较小、无残留杂质 | 158.6(0.05C)、80.8(10C)[ 160.3(0.1C)、125.4(20C)[ 158.6(0.1C)、122.6(10C)[ 140.3(0.1C)、110.6(5C)[ 150.1(0.1C)、80.6(10C)[ |
Fig. 7
(a) Schematic design of a core-shell structure; (b) Comparison of the initial charge-discharge curves at 0.1C for LiMn0.85Fe0.15PO4/C、LiMn0.67Fe0.33PO4/C、LiMn0.65Fe0.35PO4/C (non-core-shell), and LiMn0.85Fe0.15PO4 –LiFePO4/C (core-shell); (c) Comparison of the cycling performance at 0.5C for LiMn0.85Fe0.15PO4 –LiFePO4/C and LiMn0.85Fe0.15PO4 –LiFePO4/C (core-shell)[33]; (d) Schematic diagram of the Mn0.5Fe0.5C2O4·2H2O precursor; (e) Comparison of the charge-discharge curves at 0.1C for the LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 composites; (f) Comparison of ultra-long-term cycling performance at 1C[34]"
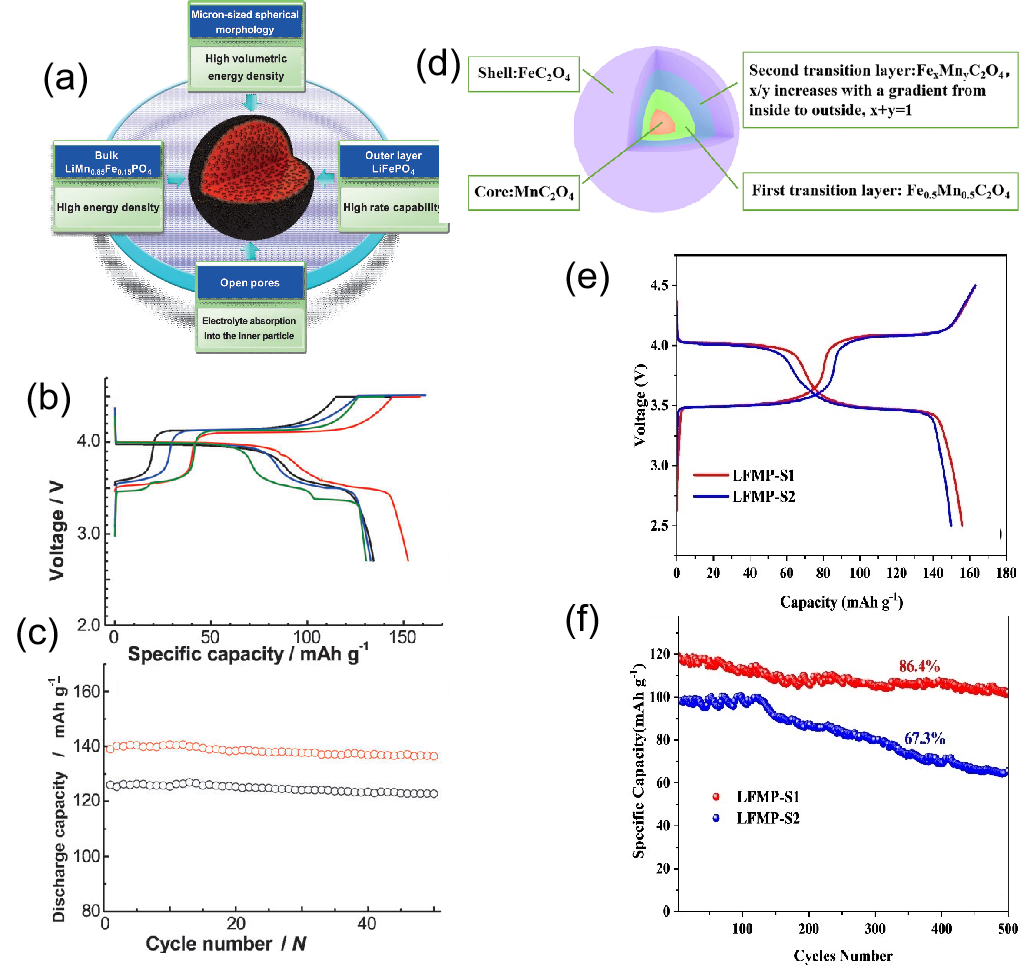
Table 2
Effect of various element doping on the performance of LiMnxFe1-xPO4/C"
| 掺杂元素 | 材料组成 | 结构影响 | 电化学性能(mAh/g) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg2+ | Li(Fe0.4Mn0.6)0.97Mg0.03PO4/C | 促进Li+迁移,降低电荷转移电阻 | 153.65(0.2C)、138.83(5C)、134.68、(10C) | [ |
| Mg2+ | LiMn0.5978Fe0.3522Mg0.0506PO4/C | 提高Li+扩散系数,降低界面电阻,抑制Jahn-Teller效应 | 150.1(0.1C)141.4(1C)111.6(5C) | [ |
| Mg2+ | LiFe0.39Mg0.01Mn0.6PO4/C | 提高电导率以及Li+扩散系数 | 158.1(0.1C)、154.6(0.5C)、131.52(5C) | [ |
| Mg2+ | LiFe0.7Mn0.25Mg0.05PO4/C | 降低材料反应的阻抗和极化,从而提高其导电性和Li+扩散系数 | 163.2(0.1C)、155.2(0.2C)、142.0(1C) | [ |
| Ni2+ | LiFe0.4Mn0.55Ni0.05PO4/C | 促进Li+迁移,降低反应极化 | 142(0.1C)、139(0.2C)、110(1C) | [ |
| Ni2+ | LiMn0.6Fe0.38Ni0.02PO4/C | 降低晶体的表面能,抑制晶体的生长,从而使晶体保持在适宜尺寸和规则形貌 | 147.3(1C)、125.1(10C)、115.4(15C) | [ |
| Ti4+ | Li(Fe0.6Mn0.4)0.97Ti0.03PO4/C | 该材料降低电位极化现象,同时其强Ti-O配位结构抑制了Jahn-Teller效应 | 163.53(0.1C)、140.59(1C)、94.08(5C) | [ |
| Nb5+ | Li0.98Mn0.6Fe0.4Nb0.02PO4/C | 减少反位缺陷,促进Li+迁移,有效地抑制Jahn-Teller效应和锰溶解 | 155.63(0.1C)、144.03(2C)、134(5C) | [ |
| Mg2+-Nb5+ | LiMn0.48Fe0.48Mg0.03Nb0.01PO4/C | 表面的Nb掺杂增强离子/电子传输,颗粒内部Mg掺杂改善Mn2+/3+氧化还原反应动力学 | 141.0(0.1C)、129.6(1C)、120.3(5C) | [ |
| V3+-Ti4+ | LiFe0.6Mn0.4PO4-V-Ti/C | 降低材料反应的阻抗和极化,增强结构稳定性,提高导电性 | 161.9(0.1C)、149.6(2C)、141.5(5C) | [ |
| [1] | ZHANG J C, LIU Z D, ZENG C H, et al. High-voltage LiCoO2 cathodes for high-energy-density lithium-ion battery [J]. RARE METALS, 2022, 41(12): 3946-56. |
| [2] | DE BIASI L, SCHWARZ B, BREZESINSKI T, et al. Chemical, structural, and electronic aspects of formation and degradation behavior on different length scales of Ni-rich NCM and Li-rich HE-NCM cathode materials in Li-Ion batteries [J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(26). |
| [3] | YI T F, ZHU Y R, ZHU X D, et al. A review of recent developments in the surface modification of LiMn2O4 as cathode material of power lithium-ion battery [J]. Ionics, 2009, 15(6): 779-84. |
| [4] | XU Z, GAO L, LIU Y, et al. Review - Recent developments in the doped LiFePO4 cathode materials for power lithium ion batteries [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2016, 163(13): A2600-A10. |
| [5] | ZHANG B K, WANG X Y, WANG S, et al. High-energy-density lithium manganese iron phosphate for lithium-ion batteries: Progresses, challenges, and prospects [J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2025, 100: 1-17. |
| [6] | XU E H, SUN X B, LYV W, et al. Optimizing the electrochemical performance of olivine LiMnxFe1-xPO4 cathode materials: Ongoing progresses and challenges [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2024, 63(22): 9631-60. |
| [7] | 文志朋, 潘凯, 韦毅, 等. 磷酸锰铁锂正极材料改性研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13: 770-787. |
| WEN Zhipeng, PAN Kai, WEI Yi, et al. Research progress on modification of lithium manganese iron phosphate cathode materials[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13: 770-787. | |
| [8] | KOPE M, YAMADA A, KOBAYASHI G, et al. Structural and magnetic properties of Lix(MnyFe1-y)PO4 electrode materials for Li-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 189(2): 1154-63. |
| [9] | YANG L, DENG W T, XU W, et al. Olivine LiMnxFe1-xPO4 cathode materials for lithium ion batteries: Restricted factors of rate performances [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(25): 14214-32. |
| [10] | DENG Y F, YANG C X, ZOU K X, et al. Recent advances of Mn-rich LiFe1-yMnyPO4 (0.5=y < 1.0) cathode materials for high energy density lithium ion batteries [J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(13). |
| [11] | LV Z, LI M, LIN J, et al. First-principles study on LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 doping to decrease the Jahn-Teller effect [J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2024, 28(2): 577-87. |
| [12] | XIN S, ZHANG H, HU Z, et al. Boosting high-temperature durability of industrial-scale LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4 cathode through niobium doping [J]. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 2025, 17(23): 33783-95. |
| [13] | RAVNSBæK D B, XIANG K, XING W T, et al. Engineering the transformation strain in LiMnyFe1-yPO4 olivines for ultrahigh rate battery cathodes [J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(4): 2375-80. |
| [14] | BHUVANESWARI D, GANGULIBABU, DOH C H, et al. Role of iron dopant and carbon additive in improving the ionic transport and electrochemical properties of LiFexMn1-xPO4 (x=0.25 and 0.75) Solid Solutions [J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2011, 6(9): 3714-28. |
| [15] | LI Y H, JIANG W W, DING G Y, et al. Hierarchically porous LiMn0.1Fe0.9PO4@C microspherical cathode materials prepared by a facile template-free hydrothermal method for high-performance lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 859. |
| [16] | LIAO L, WANG H, GUO H, et al. Facile solvothermal synthesis of ultrathin LiFexMn1-xPO4 nanoplates as advanced cathodes with long cycle life and superior rate capability [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(38): 19368-75. |
| [17] | YANG W C, BI Y J, QIN Y P, et al. LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C cathode material synthesized via co-precipitation method with superior high-rate and low-temperature performances for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 275: 785-91. |
| [18] | LIU L Y, CHEN G Y, DU B T, et al. Nano-sized cathode material LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4/C synthesized via improved sol-gel routine and its magnetic and electrochemical properties [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 255: 205-11. |
| [19] | LIU L, CAO Z, CUI Y, et al. Nanocomposites LiMnxFe1-xPO4/C synthesized via freeze drying assisted sol-gel routine and their magnetic and electrochemical properties [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 779: 339-46. |
| [20] | TUO K Y, MAO L P, DING H, et al. Boron and phosphorus dual-doped carbon coating improves electrochemical performances of LiFe0.8Mn0.2PO4 cathode materials [J]. Acs Applied Energy Materials, 2021, 4(8): 8003-15. |
| [21] | MELIGRANA G, DI LUPO F, FERRARI S, et al. Surfactant-assisted mild hydrothermal synthesis to nanostructured mixed orthophosphates LiMnyFe1-yPO4/C lithium insertion cathode materials [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 105: 99-109. |
| [22] | ZHOU G, GUO S. Comparative study on hydrothermally synthesized LiMnxFe1–xPO4 (x = 0∼1) cathode at full-cell level [J]. Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2017, 90(7): 1188-92. |
| [23] | ZUO P J, CHENG G Y, WANG L G, et al. Ascorbic acid-assisted solvothermal synthesis of LiMn0.9Fe0.1PO4/C nanoplatelets with enhanced electrochemical performance for lithium ion batteries [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 243: 872-9. |
| [24] | DU K, ZHANG L H, CAO Y B, et al. Synthesis of LiFe0.4Mn0.6-xNixPO4 /C by co-precipitation method and its electrochemical performances [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2011, 41(11): 1349-55. |
| [25] | OH S M, MYUNG S T, CHOI Y S, et al. Co-precipitation synthesis of micro-sized spherical LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 cathode material for lithium batteries [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(48): 19368-74. |
| [26] | VANAPHUTI P, SCANLAN K, MANTHIRAM A. Ammonia-free synthesis of lithium manganese iron phosphate cathodes via a co-precipitation reaction [J]. Rsc Sustainability, 2024, 2(7): 1969-78. |
| [27] | YANG L T, XIA Y G, QIN L F, et al. Concentration-gradient LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 cathode material for high performance lithium ion battery [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 304: 293-300. |
| [28] | LI Z, YOU Y, ZHU Z, et al. Surface iron concentration gradient: A strategy to suppress Mn3+ Jahn-Teller effect in lithium manganese iron phosphate [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2025, 682. |
| [29] | ZHOU X, DENG Y F, WAN L N, et al. A surfactant-assisted synthesis route for scalable preparation of high performance of LiFe0.15Mn0.85PO4/C cathode using bimetallic precursor [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 265: 223-30. |
| [30] | YANG X H, MI Y Y, ZHANG W D, et al. Enhanced electrochemical performance of LiFe0.6Mn0.4PO4/C cathode material prepared by ferrocene-assisted calcination process [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 275: 823-30. |
| [31] | LYU W, CAI W L, WANG T, et al. Thermodynamic equilibrium theory-guided design and synthesis of Mg-doped LiFe0.4Mn0.6PO4/C cathode for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2024, 91: 619-27. |
| [32] | VANAPHUTI P, MANTHIRAM A. Enhancing the Mn redox kinetics of LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 cathodes through a synergistic co-doping with niobium and magnesium for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Small, 2024, 20(47): 24048784 - 11. |
| [33] | OH S M, MYUNG S T, PARK J B, et al. Double-structured LiMn0.85Fe0.15PO4 coordinated with LiFePO4 for rechargeable lithium batteries [J]. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2012, 51(8): 1853-6. |
| [34] | JIANG X Y, LI L Y, WANG X Y, et al. Concentration-gradient structural LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4/C prepared via co-precipitation reaction for advanced lithium-ion batteries [J]. Chemphyschem, 2024, 25: e20230093051-9. |
| [35] | HU H, LI H, LEI Y, et al. Mg-doped LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C nano-plate as a high-performance cathode material for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 73: 1-8. |
| [36] | WANG Y Z, HU G R, CAO Y B, et al. Highly atom-economical and environmentally friendly synthesis of LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/rGO/C cathode material for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 354. |
| [37] | WU K P, YIN S, WANG S, et al. Construction of submicron-sized LiFe0.4Mn0.6PO4/C enwrapped into graphene framework for advanced Li-storage [J]. Carbon, 2020, 169: 55-64. |
| [38] | IVESON S M, LITSTER J D, HAPGOOD K, et al. Nucleation, growth and breakage phenomena in agitated wet granulation processes: a review [J]. Powder Technology, 2001, 117(1-2): 3-39. |
| [39] | DE YOREO J J, VEKILOV P G. Principles of crystal nucleation and growth [M]//DOVE P M, DEYOREO J J, WEINER S. Biomineralization. 2003: 57-93. |
| [40] | ERDEMIR D, LEE A Y, MYERSON A S. Nucleation of Crystals from Solution: Classical and Two-Step Models [J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2009, 42(5): 621-9. |
| [41] | WU K J, TSE E C M, SHANG C X, et al. Nucleation and growth in solution synthesis of nanostructures-From fundamentals to advanced applications [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2022, 123. |
| [42] | VOLMER M, WEBER Α. Keimbildung in übersättigten Gebilden [J]. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 1926, 119U(1): 277-301. |
| [43] | FARKAS L. Keimbildungsgeschwindigkeit in übersättigten Dämpfen [J]. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 1927, 125U(1): 236-42. |
| [44] | THANH N T K, MACLEAN N, MAHIDDINE S. Mechanisms of Nucleation and Growth of Nanoparticles in Solution [J]. Chem Rev, 2014, 114(15): 7610-30. |
| [45] | WU S Y, LI M R, SUN Y G. In Situ Synchrotron X-ray Characterization Shining Light on the Nucleation and Growth Kinetics of Colloidal Nanoparticles [J]. Angewandte Chemie-international Edition, 2019, 58(27): 8987-95. |
| [46] | 信炻江.基于共沉淀法的磷酸锰铁锂正极材料中试制备及改性 [D]. 北京:北京化工大学, 2025. |
| XIN Shijiang. Pilot-scale preparation and modification of lithium manganese iron phosphate cathode materials via coprecipitation method [D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2025. | |
| [47] | DONG H X, WANG A, SMART G, et al. In-situ analysis of nucleation and growth of transition metal oxalate battery precursor particles via time evolution of solution composition and particle size distribution [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem Eng Aspects, 2018, 558: 8-15. |
| [48] | SHEN Y D, JU X K, ZHANG J Z, et al. A convenient co-precipitation method to prepare high performance LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode for lithium ion batteries [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2020, 240. |
| [49] | 李智宇, 汤婷, 王正豪, 等. 从提钒尾液制备磷酸锰铁锂正极材料的研究 [J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2024, 45(06): 19-27. |
| LI Zhiyu, TANG Ting, WANG Zhenghao, et al. Preparation of lithium manganese iron phosphate cathode materials from vanadium extraction tail liquid [J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2024, 45(06): 19-27. | |
| [50] | 汪帆, 刘岩博, 李康丽, 等 溶液结晶中的介尺度成核过程研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 2818-2833+280. |
| WANG Fan, LIU Yanbo, LI Kangli, et al. Research progress on mesoscale nucleation processes in solution crystallization [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 2818-2833+280 | |
| [51] | 刘龙. 贫锰矿和废铁屑制备磷酸锰铁锂前驱体的研究 [D]. 东北:东北大学, 2018. |
| LIU Long. Study on the preparation of lithium manganese iron phosphate precursor from low-grade manganese ore and iron scrap chips [D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2018. | |
| [52] | SUN Y K, OH S M, PARK H K, et al. Micrometer-sized, nanoporous, high-volumetric-capacity LiMn0.85Fe0.15PO4 cathode material for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries [J]. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(43): 5050-4. |
| [53] | LI J L, XIANG M W, WANG Y, et al. Effects of adhesives on the electrochemical performance of monodisperse LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C microspheres as cathode materials for high power lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(17): 7952-60. |
| [54] | YANG L, WANG Y, WU J H, et al. Facile synthesis of micro-spherical LiMn0.7Fe0.3PO4/C cathodes with advanced cycle life and rate performance for lithium-ion battery [J]. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(6): 4821-30. |
| [55] | KOLEVA V G, BOYADZHIEVA T J, STOYANOVA R K. Crystal and morphology design of Dittmarite-type ammonium iron-manganese phosphates, NH4Mn1-xFexPO4·H2O, as precursors for phospho-olivine electrodes [J]. Crystal Growth and Design, 2019, 19(7): 3744-54. |
| [56] | REED S, SCANLAN K, MANTHIRAM A. Scalable, low-cost synthesis of high volumetric capacity LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 cathode for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2024, 12(32): 21341-9. |
| [57] | LIU W, GAO P, MI Y Y, et al. Fabrication of high tap density LiFe0.6Mn0.4PO4/C microspheres by a double carbon coating-spray drying method for high rate lithium ion batteries [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(7): 2411-7. |
| [58] | TAN Z, WANG X, ZHOU H. Highly energy density olivine cathode material synthesized by coprecipitation technique [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 90: 597-603. |
| [59] | WU J, HU L Q, HU Z, et al. Understanding the construction of nano-structured LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4 by a co-precipitation strategy and Mg2+ doping towards high-performance lithium-ion batteries [J]. Nanoscale, 2025, 17(29): 17334-44. |
| [60] | PARK Y U, KIM J, GWON H, et al. Synthesis of multicomponent olivine by a novel mixed transition metal oxalate coprecipitation method and electrochemical characterization [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2010, 22(8): 2573-81. |
| [61] | TAN Z, GAO P, CHENG F Q, et al. High power performance of multicomponent olivine cathode material for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Functional Materials Letters, 2011, 4(3): 299-303. |
| [62] | WANG L, ZHANG H Q, LI Y, et al. Improving the rate performance of LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4/C materials by the precursor method [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2022, 20: 4018-25. |
| [63] | LI Z, PANG W, TONG G, et al. Ultra-high rate and cycling performance of highly (020) preferred orientation LiMnFePO4 [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2025, 1033. |
| [64] | HU G, WANG Y, DU K, et al. Synthesis and characterization of LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/rGO/C for lithium-ion batteries via in-situ coating of Mn0.8Fe0.2C2O4·2H2O precursor with graphene oxide [J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2020, 24(10): 2441-50. |
| [65] | DU K, ZHANG L H, CAO Y B, et al. Synthesis of LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C by co-precipitation method and its electrochemical performances as a cathode material for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2012, 136(2-3): 925-9. |
| [66] | HOU P Y, ZHANG H Z, ZI Z Y, et al. Core-shell and concentration-gradient cathodes prepared via co-precipitation reaction for advanced lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(9): 4254-79. |
| [67] | OH S M, SUN Y K. Improving the electrochemical performance of LiMn0.85Fe0.15PO4-LiFePO4 core-shell materials based on an investigation of carbon source effect [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 244: 663-7. |
| [68] | CHI Z X, ZHANG W, WANG X S, et al. Accurate surface control of core-shell structured LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4@C for improved battery performance [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(41): 17359-65. |
| [69] | NGUYEN D T, KIM J, LEE Y. Design of interfacial Li-ion transfer channels for practical improvement of a multicomponent high-voltage olivine cathode [J]. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(7): 12351-60. |
| [70] | LI G H, AZUMA H, TOHDA M. Optimized LiMnyFe1-yPO4 as the cathode for lithium batteries [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2002, 149(6): A743-A7. |
| [71] | PERIYANNAN P, MUSTHAFA A M, MASILAMANI S. Synergistic design of LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 /C composites for high-performance lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials, 2025, 35(4): 1-11. |
| [72] | XIE L, CUI J W, MA Y L, et al. Microsphere LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4/C cathode with unique rod-like secondary architecture for high energy lithium ion batteries [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 499. |
| [73] | TU J, CHEN L, LI Y, et al. Effect of carbon sources on the microstructure and performance of LiFePO4 microspheres from hydrous FePO4 [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2025, 1017. |
| [74] | WANG Y, YONG F B, WANG Z H, et al. LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4/C nanoparticles via polystyrene template carburizing enhance the rate capability and capacity reversibility of cathode materials [J]. Acs Applied Nano Materials, 2024, 7(4): 4024-34. |
| [75] | FANG Z, FANG J, HU G, et al. A simple spray drying-assisted solid-state synthesis of LiFe0.67Mn0.33PO4/C cathode material for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Ionics, 2025, 31(4): 3199-208. |
| [76] | HU C L, YI H H, FANG H S, et al. Improving the electrochemical activity of LiMnPO4 via Mn-site co-substitution with Fe and Mg [J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2010, 12(12): 1784-7. |
| [77] | RAMAR V, BALAYA P. Enhancing the electrochemical kinetics of high voltage olivine LiMnPO4 by isovalent co-doping [J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2013, 15(40): 17240-9. |
| [78] | PAN C, LI B, XIE W, et al. Synergistic enhancement of lithium iron phosphate electrochemical performance by organic zinc source doping and crystalline carbon layer capping [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2024, 975. |
| [79] | 李晨威, 徐世国, 余海峰, 等. 镁掺杂改性LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4/C正极材料与性能研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 131767-74. |
| LI Chenwei, XU Shiguo, YU Haifeng, et al. Magnesium doping modification and properties of LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4/C cathode materials [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13: 1767-1774. | |
| [80] | LIU Y, CHANG C, ZHENG J. Revealing the role of Mg doping in LiFe0.39Mg0.01Mn0.6PO4/C cathode: Enhanced electrochemical performance from improved electrical conductivity and promoted lithium diffusion kinetics [J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 91. |
| [81] | XIA K, LIANG R, LUO Y, et al. Solid-State Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of Mg2+- doped LiFe0.7Mn0.3PO4/C as Cathode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries [J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2022, 17(12). |
| [82] | TIAN S Y, ZHANG K C, CAO J R, et al. Spherical Ni-doped LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4/C composites with high-rate performance [J]. Ionics, 2021, 27(7): 2877-87. |
| [83] | PENG J, LI Z, YOU Y, et al. Contribution of Ti-doping to the cyclic stability of LiFe0.6Mn0.4PO4/C [J]. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 2024, 63(18): 8228-38. |
| [84] | ZHAO M, ZHOU Y, CHEN Y, et al. Synergistic optimization of LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4 cathode material structure and electron/ion transport via trace V-Ti co-doping to achieve electrochemical performance enhancement [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2025, 35(42): 1-14. |
| [1] | Xinxin ZHANG, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Junfeng HAO, Qiangfu SUN, Bowen ZHENG, Yuhao GU, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Hong ZHOU, Xueji HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (June 1, 2025 to July 31, 2025) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(9): 3229-3248. |
| [2] | Junfeng HAO, Jing ZHU, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Xinxin ZHANG, Qiangfu SUN, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Hong ZHOU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Apr. 1, 2025 to May 31 2025) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(7): 2884-2902. |
| [3] | Dandan HAN, Wuwei ZHANG, Liang ZHANG, Zongjiang WANG. Design and electrochemical performance of LiMn1-y Fe y PO4/C cathode materials with a core-shell structure [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(6): 2215-2222. |
| [4] | Qiangfu SUN, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Jing ZHU, Junfeng HAO, Xinxin ZHANG, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Hong ZHOU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Feb. 1, 2025 to March 31, 2025) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(5): 1727-1747. |
| [5] | Xinxin ZHANG, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Jing ZHU, Junfeng HAO, Qiangfu SUN, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Hong ZHOU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of 100 selected recent papers on lithium batteries (December 1, 2024 to January 31, 2025) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(3): 1310-1330. |
| [6] | Boyu LIU, Tengfei WANG, Qing PANG, Kaiyu CHEN, Hongyu WANG. Preparation and electrochemical performance of Mg-Cr co-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(3): 1097-1106. |
| [7] | Lishuai ZHANG, Yifei ZHANG, Yiyang MA, Sibo ZHAO, Hongquan LIU, Shengting SHI, Yanjun ZHONG. Research progress on sodium-ion battery cathode materials based on iron-based prussian blue analogues [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(2): 525-543. |
| [8] | Junfeng HAO, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Jing ZHU, Qiangfu SUN, Xinxin ZHANG, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Hong ZHOU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Oct. 1, 2024 to Nov. 30, 2024) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(1): 388-405. |
| [9] | Xinxin ZHANG, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Jing ZHU, Junfeng HAO, Qiangfu SUN, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Hong ZHOU, Xueji HUANG. In-depth review of 100 pioneering studies on lithium batteries: Key innovations from June 1, 2024 to July 31, 2024 [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(9): 3226-3244. |
| [10] | Xiaoyu CHEN, Yu LIU, Yifan BAI, Jiajun YING, Ying LV, Lijia WAN, Junping HU, Xiaoling Chen. Preparation and performance of nickel cobalt hydroxide cathode material for nickel zinc batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2377-2385. |
| [11] | Weiqi LIN, Qiaoyu LU, Yuhong CHEN, Linyuan QIU, Yurong JI, Lianyu GUAN, Xiang DING. Advances in cathode materials for low-temperature sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2348-2360. |
| [12] | Junfeng HAO, Jing ZHU, Xiaoyu SHEN, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Xinxin ZHANG, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Qiangfu SUN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. A review of 100 selected recent studies on lithium batteries (April 1, 2024—May 31, 2024) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2361-2376. |
| [13] | Wanrui LI, Wenjun LI, Xiaoqing WANG, Shengli LU, Xilian XU. Research progress of manganese/vanadium-based oxide heterostructure cathodes for zinc-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(5): 1496-1515. |
| [14] | Yinbao MIAO, Wenhua ZHANG, Weihao LIU, Shuai WANG, Zhe CHEN, Wang PENG, Jie ZENG. Preparation and performance of lithium-rich cathode material Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(5): 1427-1434. |
| [15] | Jing ZHU, Junfeng HAO, Qiangfu SUN, Xinxin ZHANG, Xiaoyu SHEN, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Feb. 1, 2024 to Mar. 31, 2024) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(5): 1398-1416. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
