Energy Storage Science and Technology ›› 2024, Vol. 13 ›› Issue (10): 3453-3466.doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2024.0348
• Energy Storage Materials and Devices • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yukun WANG1,2( ), Xuelian LI1,2,3(
), Xuelian LI1,2,3( ), Puying LEI1,2, Kai QI1,2, Lili GAO1,2(
), Puying LEI1,2, Kai QI1,2, Lili GAO1,2( ), Zhuanpei WANG4, Xiaowei YANG4,5
), Zhuanpei WANG4, Xiaowei YANG4,5
Received:2024-04-22
Revised:2024-05-15
Online:2024-10-28
Published:2024-10-30
Contact:
Xuelian LI, Lili GAO
E-mail:wangyukun1156@link.tyut.edu.cn;lixuelian@tyut.edu.cn;gaolili@tyut.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Yukun WANG, Xuelian LI, Puying LEI, Kai QI, Lili GAO, Zhuanpei WANG, Xiaowei YANG. Cathode catalysts for Li-CO2 battery: Development and challenges[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(10): 3453-3466.

Fig. 2
SEM images of CNTs cathodes in different states: pristine (a);after discharge at different current densities: 50 (b), 100 (c), and 150 mA/g (d) with a cut-off capacity of 1000 mAh/g[15];(e) Adsorption energies of graphene, graphitic-N, pyrrolic-N, and pyridinic-N for CO2, Li, and Li2CO3[16];(f) Schematic for the preparation of B-NCNT cathode by floating catalyst chemical vapor deposition[13];(g), (h) SEM and (i) TEM images of 3D NCNT/G[17]; (j) The charge-discharge overpotential as a function of the adsorption energy of *CO intermediate[20]"
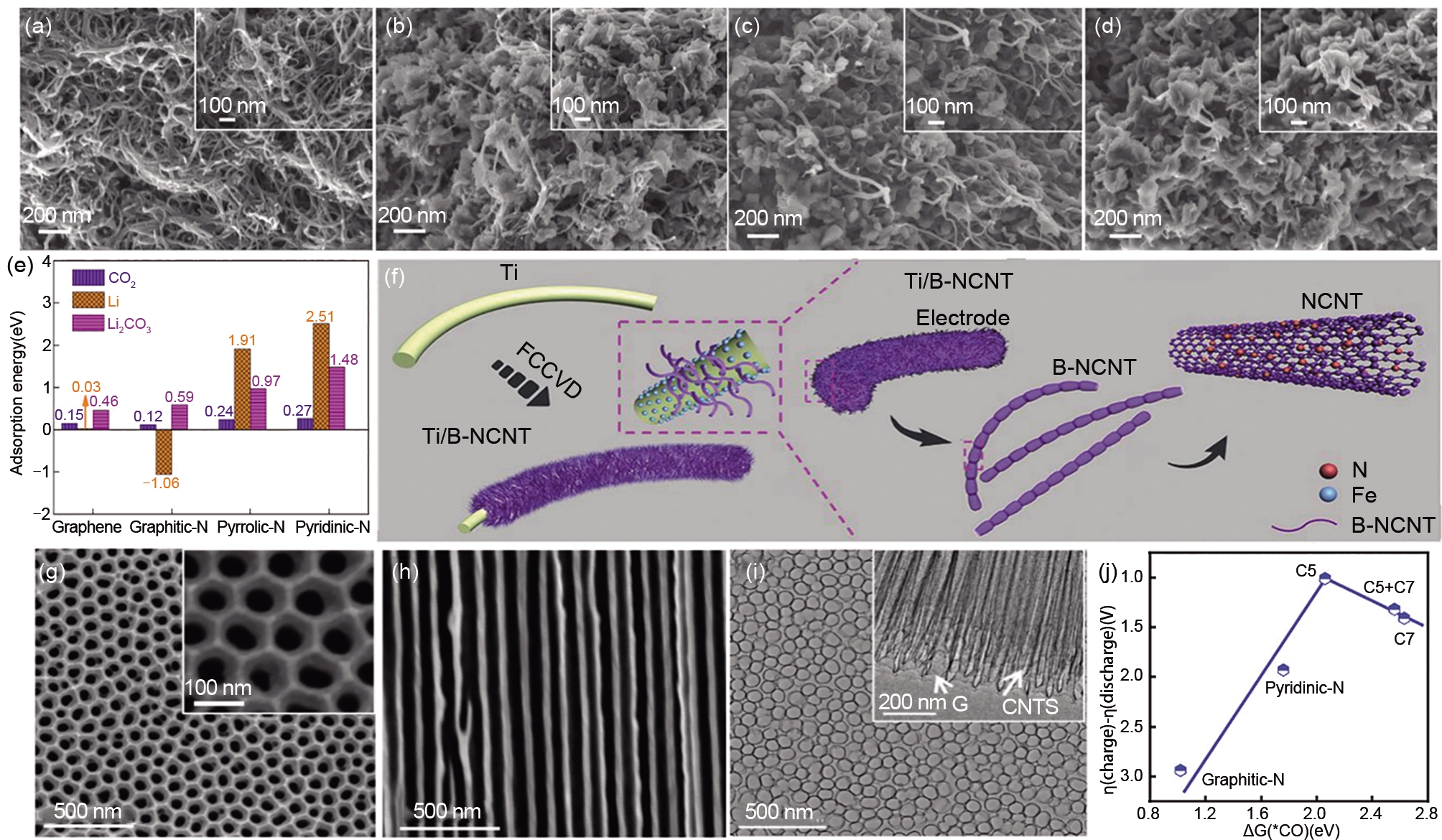

Fig. 3
(a) Schematic of the reaction mechanism of Li-CO2 batteries and (b), (c) in-situ SERS spectra with and without Ru catalysts[11];(d) Finite difference time domain simulations and schematics of the charge carrier migration of TNAs and TNAs@AgNPs. E0 and E represent the intensities of the incident and localized electric field, respectively;(e) Mechanism of the dual-field assisted Li-CO2 battery[26];HRTEM images of Ru NPs (f) and Ni/Ru HNPs (g) in Ru(10-10) and Ru(0002);(h) The Projected Density of State of Ru 4d orbital on Ni/Ru (0002) and pristine Ru (0002) (Dashed lines indicate the d-band centers)[29]"


Fig. 4
(a) The planar-averaged charge density difference (Δρz) for the Fe2O3/Cu2O sample; (b) Schematic diagram of the catalytic mechanism of Fe2O3/Cu2O/Cu[36];Mo 3d XPS spectra after 1st discharge (c) and 1st recharge (d) of Mo2N@HsGDY[37];SEM image (e) and illustration (f) of V-MoS2/Co9S8@CP with MoS2 vertically grows on Co9S8 with an interface along the edge;(g) Gibbs free energy changes at the rate-determining step of MoS2 basal plane, MoS2 edge and Co9S8[38]"


Fig. 5
(a) Atomic-resolution STEM image, (b) Fe K-edge XANES and (c) EXAFS of Fe-ISA/N,S-HG[40];(d) Schematic illustrations of Fe-N-C catalysts[42];Work function profiles of (e) Co4N (111) and (f) Cu-Co4N (111) surface[44];(g), (h) SEM images of Runp-NC@rGO (Nanoparticle) and Ruh-NC@rGO (Single-Atom) discharged cathode[43];(i) Li2C2O4 adsorption configurations on oxygen group-doped Mn-N4 sites and on N,O-doped graphene[45]"


Fig. 6
(a) CV curves of Li-CO2 batteries with LiBr and (b) schematic diagram of the charging mechanism of Li-CO2 battery;(c) Charge-discharge polarization curves of Li-CO2 batteries with addition of LiBr as RMs[46];(d) Mechanism of Cu(I)-RMs-mediated CO2RR[48];(e) Mechanism diagram of RM(II)-BTC-mediated Li2C2O4 product generation[49]"

| 1 | ZHANG X, ZHANG Q, ZHANG Z, et al. Rechargeable Li-CO2 batteries with carbon nanotubes as air cathodes[J]. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(78): 14636-14639. DOI: 10.1039/c5cc05767a. |
| 2 | TAKECHI K, SHIGA T, ASAOKA T. A Li-O2/CO2 battery[J]. Chemical Communications, 2011, 47(12): 3463. DOI: 10.1039/c0cc05176d. |
| 3 | XU S M, DAS S K, ARCHER L A. The Li-CO2 battery: A novel method for CO2 capture and utilization[J]. RSC Advances, 2013, 3(18): 6656-6660. DOI: 10.1039/C3RA40394G. |
| 4 | HOU Y Y, WANG J Z, LIU L L, et al. Mo2C/CNT: An efficient catalyst for rechargeable Li-CO2 batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017, 27(27): 1700564. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201700564. |
| 5 | XIE J F, LIU Q, HUANG Y Y, et al. A porous Zn cathode for Li-CO2 batteries generating fuel-gas CO[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(28): 13952-13958. DOI: 10.1039/C8TA02771D. |
| 6 | ZHAO Z W, HUANG J, PENG Z Q. Achilles' heel of lithium–air batteries: Lithium carbonate[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(15): 3874-3886. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201710156. |
| 7 | MEINI S, TSIOUVARAS N, SCHWENKE K U, et al. Rechargeability of Li-air cathodes pre-filled with discharge products using an ether-based electrolyte solution: Implications for cycle-life of Li-air cells[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2013, 15(27): 11478-11493. DOI: 10.1039/c3cp51112j. |
| 8 | LI S W, DONG Y, ZHOU J W, et al. Carbon dioxide in the cage: Manganese metal-organic frameworks for high performance CO2 electrodes in Li-CO2 batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(5): 1318-1325. DOI: 10.1039/C8EE00415C. |
| 9 | YANG S X, HE P, ZHOU H S. Exploring the electrochemical reaction mechanism of carbonate oxidation in Li-air/CO2 battery through tracing missing oxygen[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2016, 9(5): 1650-1654. DOI: 10.1039/c6ee00004e. |
| 10 | QIAO Y, YI J, WU S C, et al. Li-CO2 electrochemistry: A new strategy for CO2 fixation and energy storage[J]. Joule, 2017, 1(2): 359-370. DOI: 10.1016/j.joule.2017.07.001. |
| 11 | YANG S X, QIAO Y, HE P, et al. A reversible lithium-CO2 battery with Ru nanoparticles as a cathode catalyst[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2017, 10(4): 972-978. DOI: 10.1039/C6EE03770D. |
| 12 | QI G C, ZHANG J X, CHEN L, et al. Binder-free MoN nanofibers catalysts for flexible 2-electron oxalate-based Li-CO2 batteries with high energy efficiency[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(22): 2112501. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202112501. |
| 13 | LI X L, ZHOU J W, ZHANG J X, et al. Bamboo-like nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube forests as durable metal-free catalysts for self-powered flexible Li-CO2 batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(39): e1903852. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201903852. |
| 14 | MA L T, FAN H Q, WANG J, et al. Water-assisted ions in situ intercalation for porous polymeric graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets with superior photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2016, 190: 93-102. DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.03.002. |
| 15 | XIAO X, TAN P, ZHU X B, et al. Investigation on the discharge and charge behaviors of Li-CO2 batteries with carbon nanotube electrodes[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 8(26): 9742-9750. DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c01863. |
| 16 | CHEN B, WANG D S, ZHANG B, et al. Engineering the active sites of graphene catalyst: From CO2 activation to activate Li-CO2 batteries[J]. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(6): 9841-9850. DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.1c00756. |
| 17 | XIAO Y, DU F, HU C G, et al. High-performance Li-CO2 batteries from free-standing, binder-free, bifunctional three-dimensional carbon catalysts[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2020, 5(3): 916-921. DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.0c00181. |
| 18 | YU W, LIU L M, YANG Y X, et al. N, O-diatomic dopants activate catalytic activity of 3D self-standing graphene carbon aerogel for long-cycle and high-efficiency Li-CO2 batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 465: 142787. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.142787. |
| 19 | SONG L, HU C G, XIAO Y, et al. An ultra-long life, high-performance, flexible Li-CO2 battery based on multifunctional carbon electrocatalysts[J]. Nano Energy, 2020, 71: 104595. DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.104595. |
| 20 | YE F H, GONG L L, LONG Y D, et al. Topological defect-rich carbon as a metal-free cathode catalyst for high-performance Li-CO2 batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(30): 2101390. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202101390. |
| 21 | HAN J R, WU H Y, SONG R L, et al. Defect-rich porous carbon as a metal-free catalyst for high-performance Li-CO2 batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2024, 477: 143779. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2024.143779. |
| 22 | LI J X, ZHANG K, ZHAO Y, et al. High-efficiency and stable Li-CO2 battery enabled by carbon nanotube/carbon nitride heterostructured photocathode[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed), 2022, 61(4): e202114612. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202114612. |
| 23 | XING Y, WANG K, LI N, et al. Ultrathin RuRh alloy nanosheets enable high-performance lithium-CO2 battery[J]. Matter, 2020, 2(6): 1494-1508. DOI: 10.1016/j.matt.2020.02.020. |
| 24 | ZHANG Z, YANG C, WU S S, et al. Exploiting synergistic effect by integrating ruthenium-copper nanoparticles highly co-dispersed on graphene as efficient air cathodes for Li-CO2 batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(8): 1802805. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201802805. |
| 25 | XING Y, YANG Y, LI D H, et al. Crumpled Ir nanosheets fully covered on porous carbon nanofibers for long-life rechargeable lithium-CO2 batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(51): e1803124. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201803124. |
| 26 | ZHANG K, LI J X, ZHAI W J, et al. Boosting cycling stability and rate capability of Li-CO2 batteries via synergistic photoelectric effect and plasmonic interaction[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(17): e202201718. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202201718. |
| 27 | GUAN D H, WANG X X, LI F, et al. All-solid-state photo-assisted Li-CO2 battery working at an ultra-wide operation temperature[J]. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(8): 12364-12376. DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.2c03534. |
| 28 | GUO Z Y, LI J L, QI H C, et al. A highly reversible long-life Li-CO2 battery with a RuP2-based catalytic cathode[J]. Small, 2019, 15(29): 1803246. DOI: 10.1002/smll.201803246. |
| 29 | FAN L, SHEN H M, JI D X, et al. Biaxially compressive strain in Ni/Ru core/shell nanoplates boosts Li-CO2 batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(30): 2204134. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202204134. |
| 30 | ZHANG X, WANG C Y, LI H H, et al. High performance Li-CO2 batteries with NiO-CNT cathodes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(6): 2792-2796. DOI: 10.1039/C7TA11015D. |
| 31 | ZHANG Z, WANG X G, ZHANG X, et al. Verifying the rechargeability of Li-CO2 batteries on working cathodes of Ni nanoparticles highly dispersed on N-doped graphene[J]. Advanced Science, 2018, 5(2): 1700567. DOI: 10.1002/advs.201700567. |
| 32 | ZHENG R X, SHU C Z, LI J B, et al. Oxygen vacancy engineering of vertically aligned NiO nanosheets for effective CO2 reduction and capture in Li-CO2 battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 383: 138359. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2021.138359. |
| 33 | LIU L M, SHEN S Y, ZHAO N, et al. Revealing the indispensable role of in situ electrochemically reconstructed Mn(II)/Mn(III) in improving the performance of lithium-carbon dioxide batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(26): 2403229. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202403229. |
| 34 | LI S W, LIU Y, ZHOU J W, et al. Monodispersed MnO nanoparticles in graphene-an interconnected N-doped 3D carbon framework as a highly efficient gas cathode in Li-CO2 batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 12(3): 1046-1054. DOI: 10.1039/C8EE03283A. |
| 35 | LIU Y Q, SHU P F, ZHANG M T, et al. Uncovering the geometry activity of spinel oxides in Li-CO2 battery reactions[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2024, 9(5): 2173-2181. DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.4c00603. |
| 36 | ZHU Y B, WEI Y, LI P Z, et al. Type-II heterojunction photocathode for CO2 reduction and light-assisted metal-CO2 batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2024, 12(9): 5133-5144. DOI: 10.1039/D3TA07450A. |
| 37 | ZHANG J X, QI G C, CHENG J L, et al. Boosted reaction kinetics of Li-CO2 batteries by atomic layer-deposited Mo2N on hydrogen substituted graphdiyne[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2023, 11(45): 16185-16193. DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.3c04090. |
| 38 | LU B Y, CHEN B, WANG D S, et al. Engineering the interfacial orientation of MoS2/Co9S8 bidirectional catalysts with highly exposed active sites for reversible Li-CO2 batteries[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2023, 120(6): e2216933120. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2216933120. |
| 39 | ZHAO J Y, WANG Y, ZHAO H Y, et al. Enabling all-solid-state lithium-carbon dioxide battery operation in a wide temperature range[J]. ACS Nano, 2024, 18(6): 5132-5140. DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.3c12522. |
| 40 | HU C G, GONG L L, XIAO Y, et al. High-performance, long-life, rechargeable Li-CO2 batteries based on a 3D holey graphene cathode implanted with single iron atoms[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(16): e1907436. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201907436. |
| 41 | XU Y Y, JIANG C, GONG H, et al. Single atom site conjugated copper polyphthalocyanine assisted carbon nanotubes as cathode for reversible Li-CO2 batteries[J]. Nano Research, 2022, 15(5): 4100-4107. DOI: 10.1007/s12274-021-4052-1. |
| 42 | DING J C, XUE H R, XIAO R, et al. Atomically dispersed Fe-Nx species within a porous carbon framework: An efficient catalyst for Li-CO2 batteries[J]. Nanoscale, 2022, 14(12): 4511-4518. DOI: 10.1039/D1NR08354F. |
| 43 | CHENG J, BAI Y Q, LIAN Y B, et al. Homogenizing Li2CO3 nucleation and growth through high-density single-atomic Ru loading toward reversible Li-CO2 reaction[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(16): 18561-18569. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.2c02249. |
| 44 | MA X Y, ZHAO W T, DENG Q H, et al. In-situ construction of Cu-Co4N@CC hierarchical binder-free cathode for advanced and flexible Li-CO2 batteries: Electron structure and mass transfer modulation[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 535: 231446. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2022.231446. |
| 45 | WANG M L, YAO Y, TIAN Y H, et al. Atomically dispersed manganese on carbon substrate for aqueous and aprotic CO2 electrochemical reduction[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(12): e2210658. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202210658. |
| 46 | WANG X G, WANG C Y, XIE Z J, et al. Improving electrochemical performances of rechargeable Li-CO2 batteries with an electrolyte redox mediator[J]. ChemElectr℃hem, 2017, 4(9): 2145-2149. DOI: 10.1002/celc.201700539. |
| 47 | SHIGA T, KATO Y, INOUE M, et al. Bifunctional catalytic activity of iodine species for lithium-carbon dioxide battery[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2019, 7(16): 14280-14287. DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b03949. |
| 48 | SUN X Y, MU X W, ZHENG W, et al. Binuclear Cu complex catalysis enabling Li-CO2 battery with a high discharge voltage above 3.0 V[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 536. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-36276-8. |
| 49 | LI W, ZHANG M H, SUN X Y, et al. Boosting a practical Li-CO2 battery through dimerization reaction based on solid redox mediator[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 803. DOI: 10. 1038/s41467-024-45087-4. |
| [1] | Xinxin ZHANG, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Jing ZHU, Junfeng HAO, Qiangfu SUN, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Hong ZHOU, Xueji HUANG. In-depth review of 100 pioneering studies on lithium batteries: Key innovations from June 1, 2024 to July 31, 2024 [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(9): 3226-3244. |
| [2] | Xiaoyu CHEN, Yu LIU, Yifan BAI, Jiajun YING, Ying LV, Lijia WAN, Junping HU, Xiaoling Chen. Preparation and performance of nickel cobalt hydroxide cathode material for nickel zinc batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2377-2385. |
| [3] | Meilong WANG, Yurui XUE, Wenxi HU, Keyu DU, Ruitao SUN, Bin ZHANG, Ya YOU. Design and research of all-ether high-entropy electrolyte for low-temperature lithium iron phosphate batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2131-2140. |
| [4] | Weiqi LIN, Qiaoyu LU, Yuhong CHEN, Linyuan QIU, Yurong JI, Lianyu GUAN, Xiang DING. Advances in cathode materials for low-temperature sodium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2348-2360. |
| [5] | Junfeng HAO, Jing ZHU, Xiaoyu SHEN, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Xinxin ZHANG, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Qiangfu SUN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. A review of 100 selected recent studies on lithium batteries (April 1, 2024—May 31, 2024) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(7): 2361-2376. |
| [6] | Yuchao ZHANG, Fengjiao ZHANG, Wei LOU, Feixiang ZAN, Linling WANG, Anxu SHENG, Xiaohui WU, Jing CHEN. Transformation process of valuable metals in the recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries and the potential environmental impact [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(6): 1861-1870. |
| [7] | Wanrui LI, Wenjun LI, Xiaoqing WANG, Shengli LU, Xilian XU. Research progress of manganese/vanadium-based oxide heterostructure cathodes for zinc-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(5): 1496-1515. |
| [8] | Yinbao MIAO, Wenhua ZHANG, Weihao LIU, Shuai WANG, Zhe CHEN, Wang PENG, Jie ZENG. Preparation and performance of lithium-rich cathode material Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(5): 1427-1434. |
| [9] | Yuanyuan JIANG, Fangfang TU, Fangping ZHANG, Yinglai WANG, Jiawen CAI, Donghui YANG, Yanhong LI, Jiayuan XIANG, Xinhui XIA, Jipeng FU. Study on technology and mechanism of prelithiation for high-performance lithium iron phosphate battery [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(5): 1435-1442. |
| [10] | Xinyu LIU, Anan ZHANG, Changjiang LIAO. Numerical simulation analysis of solid oxide fuel cells with different support structures [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(5): 1710-1720. |
| [11] | Jing ZHU, Junfeng HAO, Qiangfu SUN, Xinxin ZHANG, Xiaoyu SHEN, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Feb. 1, 2024 to Mar. 31, 2024) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(5): 1398-1416. |
| [12] | Meiling WU, Lei NIU, Shiyou LI, Dongni ZHAO. Research progress on cathode prelithium additives used in lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(3): 759-769. |
| [13] | Qiangfu SUN, Xiaoyu SHEN, Guanjun CEN, Ronghan QIAO, Jing ZHU, Junfeng HAO, Xinxin ZHANG, Mengyu TIAN, Zhou JIN, Yuanjie ZHAN, Yong YAN, Liubin BEN, Hailong YU, Yanyan LIU, Xuejie HUANG. Reviews of selected 100 recent papers for lithium batteries (Dec. 1, 2023 to Jan. 31, 2024) [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(3): 725-741. |
| [14] | Ke PENG, Zhicheng ZHANG, Youzhang HU, Xuhui ZHANG, Jiahui ZHOU, Bin LI. Finite element-based motion analysis and optimization of sagger in thermo-mechanical coupling field [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(2): 634-642. |
| [15] | Xiuli GUO, Xiaolong ZHOU, Caineng ZOU, Yongbing TANG. Research progress and perspectives of aqueous dual-ions batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(2): 462-479. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
